FIGURE 10.
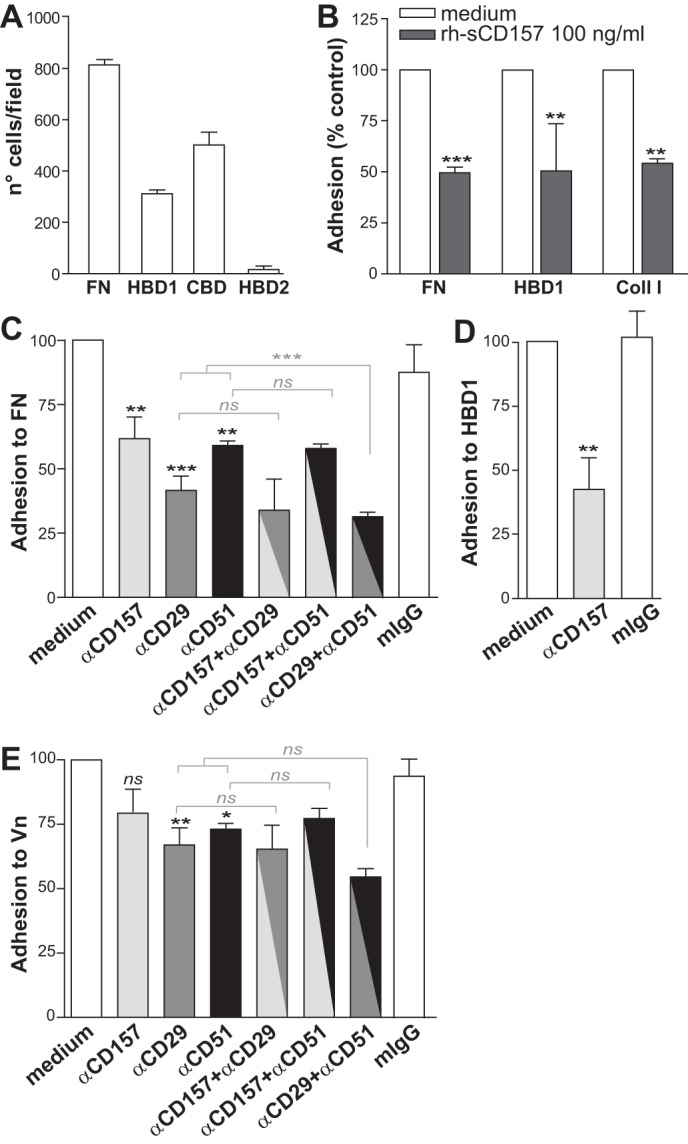
CD157 controls the adhesion of mesothelial cells to extracellular matrix proteins. A, Met-5A cells were plated on full-length fibronectin or on its proteolytic fragments for 2 h. B, ability of membrane CD157 and rh-sCD157 to bind the same sites on FN, HBD1, and Coll I was evaluated by assessing the adhesion efficiency of Met-5A cells to each protein after saturation with rh-sCD157 (100 ng/ml). Results are expressed as percentage of controls (cell adhesion to coated proteins without saturation with rh-sCD157 = 100%, white histogram). ***, p < 0.001; **, p < 0.01, unpaired t test. C–E, ability of membrane CD157 to bind full-length fibronectin, HBD1, and Vn was evaluated in the presence or absence of the RF3 anti-CD157, anti-CD29, or anti-CD51 blocking mAbs (either alone or in combination) or irrelevant murine IgG (10 μg/ml). Results are expressed as percentage of control (number of adherent cells in the absence of antibody = 100%, white histogram). ***, p < 0.001; **, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05, ns, not significant, ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple comparison test. Cells were plated for FN, HBD1, Coll, or Vn, and then adherent cells were fixed with 4% PFA, stained with 0.5% crystal violet, and counted by light microscopy in five randomly selected fields (×4) for each well. Results represent the mean values ± S.E. of at least three experiments performed in triplicate.
