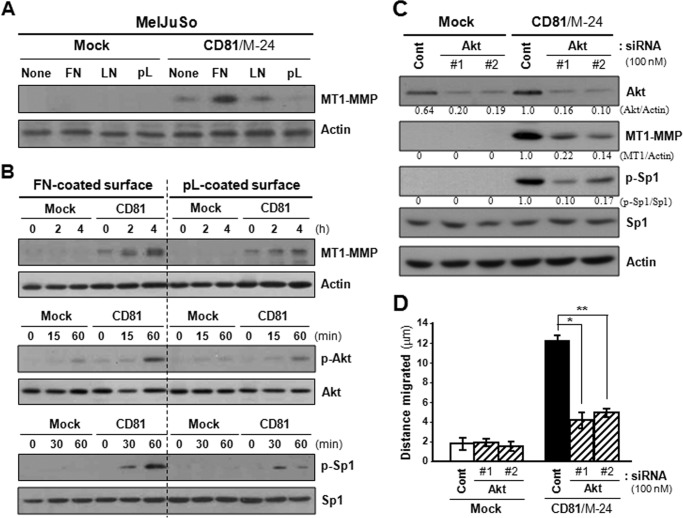
FIGURE 9.
Integrin-dependent CD81 signaling activates Akt, which up-regulates Sp1-mediated MT1-MMP expression and cell motility. A, MelJuSo mock and CD81 transfectant cells were suspended in serum-free medium for 60 min and seeded onto plates precoated with fibronectin (FN), laminin (LN), or poly-l(+)-lysine (pL). Following 24-h culture, cells were examined for MT1-MMP expression using immunoblotting analysis. B, cells in suspension were seeded onto fibronectin- or poly-l(+)-lysine-coated plate for the indicated time period and then examined for protein levels of MT1-MMP, Akt, and Sp1. Phosphorylation levels of Akt and Sp1 were also assessed by immunoblotting analyses using anti-phospho-AktSer-473 and phospho-Sp1Thr-453 antibodies, respectively. Shown are representative immunoblots of three independent experiments. C and D, cells grown on fibronectin-coated plate were transfected with two siRNAs targeting Akt and then examined for MT1-MMP protein and Sp1 phosphorylation levels (C) and cell motility (D). The protein levels of Akt and MT1-MMP and phosphorylation levels of Sp1 were normalized to actin and Sp1 protein levels, respectively. Mean values of relative band intensity are shown under the immunoblot. Migration data shown are the mean ± S.D. from three separate experiments with three determinations per experiment (* and **, p < 0.01). Error bars represent S.D. Cont, control.