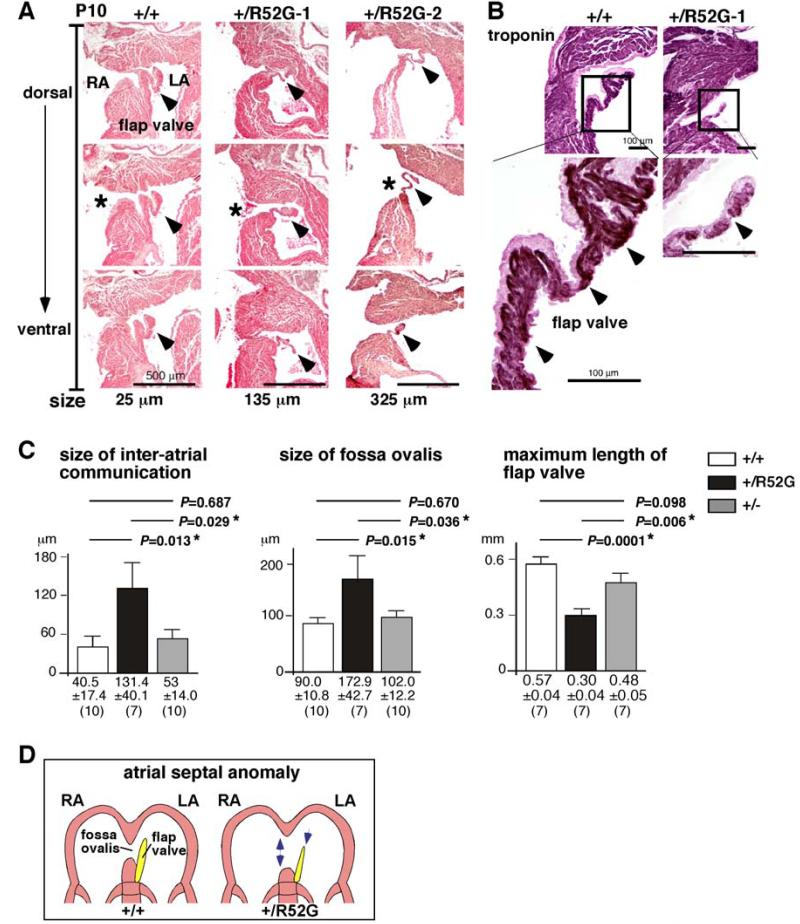
Figure 6. Inter-atrial communication in P10 Nkx2-5+/R52G hearts compared to age-matched Nkx2-5+/+ or Nkx2-5+/− hearts.
(A) Representative histological sections from P10 mouse hearts selected for a total of 25 μm (5 sections, 5 μm thickness) from Nkx2-5+/+ mouse, and for 135 μm or 325 μm from two Nkx2-5+/R52G mice. Asterisks indicate open inter-atrial communication. Arrowheads indicate flap valve. Dorsal/posterior (top panel) to ventral/anterior sections (bottom panel) are shown. (B) Immunostaining of troponin T (brown) with counter-staining with eosin (pink). (C) Size of inter-atrial communication, fossa ovalis and maximum length of flap valve calculated from a number of tissue sections (5 μm per section). The number of mice examined is indicated. ANOVA demonstrated significant differences among the three groups (F = 4.04, 3.77, 12.03; P = 0.031, 0.038, 0.000, respectively). Of note, maximum length of flap valve from three heart sections each from Nkx2-5+/+ and Nkx2-5+/− could not be measured because flap valve and septum secundum were fused. (D) Simplified illustrations of the atrial septal structure in Nkx2-5+/+ vs. Nkx2-5+/R52G.