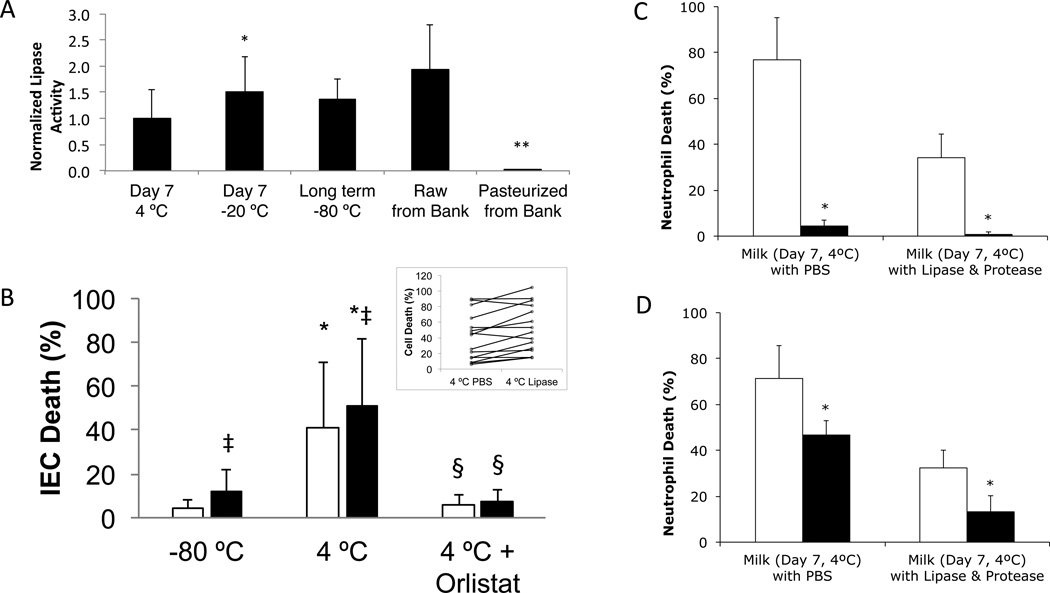
Figure 2. IEC death after 4 °C storage, lipase activity and effects of lipase inhibition or hydrophobic filtering on cell death.
(A) Milks stored (duration and temperature as shown) or obtained from the milk bank before and after pasteurization. Values normalized by activity prior to storage (or the mean of the fresh milk activity, in the case of DM). N=12 donors of fresh milk, N=6 batches of raw DM and 6 batches of pasteurized DM. * p < 0.0007 vs. Day 7 4°C milk. **p< 0.003 vs. raw milk or Day 7 4°C milk. (B) Milk stored at −80 °C or 7 days at 4 °C (with or without orlistat) before transfer to −80 °C (total storage time 13 ± 5 days – min 7, max 20), then digested (PBS (white) or 0.1 mg/ml lipase (black)) and exposed to IEC for 5 minutes. N=15; ‡ p<0.006 vs. without lipase; * p<0.0007 vs. −80 °C storage only; § p<0.0007 vs. without orlistat. Inset: raw data from Day 7 4°C milk digested with PBS or Lipase. (C&D) Milk stored 7 days at 4 °C (non-cytotoxic samples excluded) (C) with (black) or without (white) orlistat pretreatment or (D) before (white) or after (black) removing unbound FFAs by filtering three times with glass fibers. (C) * p<0.02 (N=3 for milk w/ PBS; N=4 for milk w/ lipase and protease groups), (D) * p<0.05 (N=3 in milk w/ PBS; N=5 in milk w/ lipase and protease).