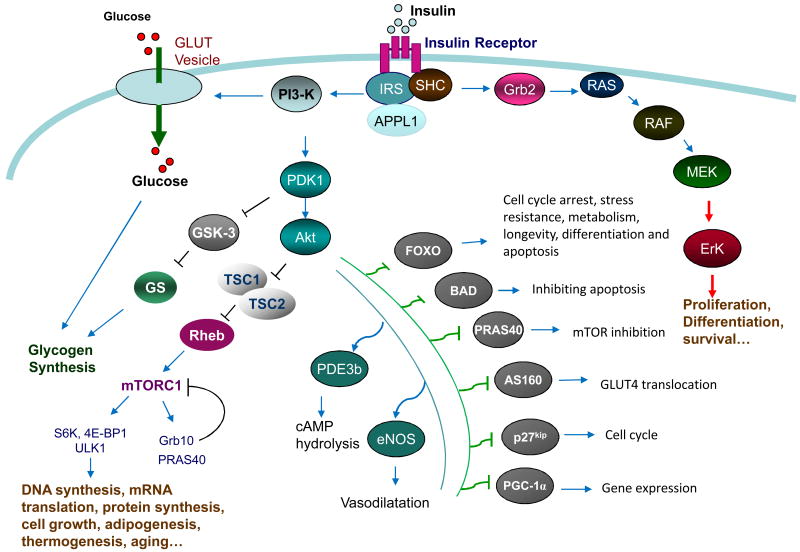
Figure 1. Insulin signaling and function.
The binding of insulin to its receptor on cell membrane results in insulin receptor (IR) tyrosine kinase activation and IR tyrosine phosphorylation. APPL1 functions as a piggyback protein that promotes IRS binding to the tyrosine phosphorylated IR, leading to IRS tyrosine phosphorylation and subsequent activation of the PI3K/PDK1/Akt signaling pathway. Activation of Akt promotes the phosphorylation and inhibition of TSC1/2, a negative regulator of the mTORC1 signaling pathway. Akt also phosphorylates many other cellular proteins and plays key roles in various cellular events. Tyrosine phosphorylation of IR promotes the association of the adaptor proteins Shc and Grb2 to the IR, leading to the activation of the RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK1/2 cascade, which is essential for cell growth, differentiation and protein synthesis.