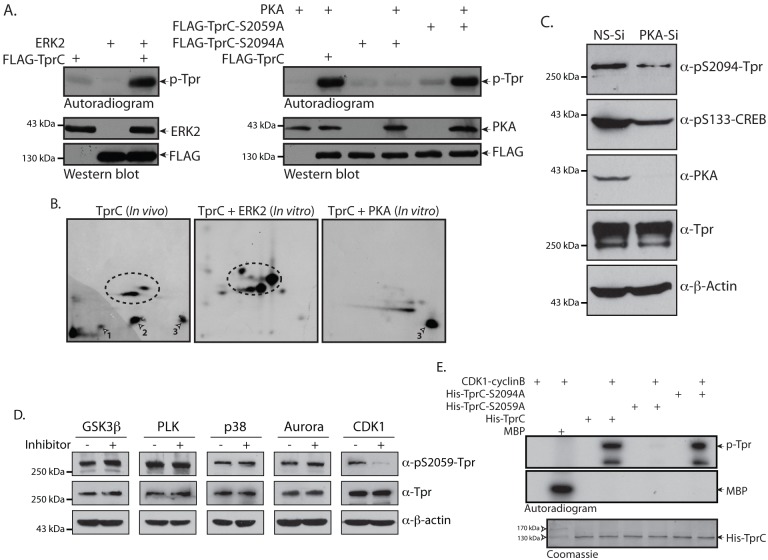
Fig. 4.
PKA and CDK1 phosphorylate Tpr at residues S2094 and S2059, respectively. (A) COS-1 cells were transfected with 8 µg each of constructs encoding wild-type FLAG–TprC, FLAG–TprC-S2059A, FLAG–TprC-S2094A, HA–ERK2 and CMV-PKA. The lysates of cell obtained at 36 h post-transfection were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG, anti-HA or anti-PKA antibodies. The immunoprecipitated FLAG–TprC or CMV-PKA were mixed either with immunoprecipitated HA–ERK2 or with FLAG–TprC, FLAG–TprC-S2059A or FLAG–TprC-S2094A samples, respectively, and kinase reactions were performed in the presence of [γ-32P]-ATP at 30°C for 10 min. (B) TprC phosphorylated in vitro by either ERK2 or PKA was digested with trypsin, and the resulting phosphopeptides were mapped by 2D-TLC. A comparative peptide map of the in-vivo-labeled TprC protein is also shown. Arrowheads show the ERK-independent tryptic phosphopeptides; dotted circles show ERK-mediated phosphorylation. (C) COS-1 cells were transfected with either NS-siRNA (NS-Si) or PKA-specific siRNA (PKA-Si) and, 96 h post-transfection, cell lysates were probed with anti-PKA, anti-β-actin, anti-CREB-pS133, anti-Tpr and anti-Tpr-pS2094 antibodies. (D) HeLa cells were treated with inhibitors against GSK3β (Inhibitor VIII; 10 µM), PLK (BI2536; 100 nM), p38 (SB203580; 20 µM), Aurora kinase (MLN8237; 500 nM) and CDK1 (RO3306; 10 µM) for 2 h. Cells were lysed in 2× SDS sample buffer and the lysates were then probed with anti-Tpr, anti-Tpr-pS2059 and anti-β-actin antibodies. (E) Wild-type His–TprC and the phospho-mutants His–TprC-S2059A and His–TprC-S2094A were purified from E.coli. The proteins were incubated with CDK1–cyclinB complex and kinase reactions were carried out in the presence of [γ-32P]-ATP at 30°C for 10 min. The autoradiogram is shown, along with Coomassie Blue staining to visualize protein loading.