Fig. 1.
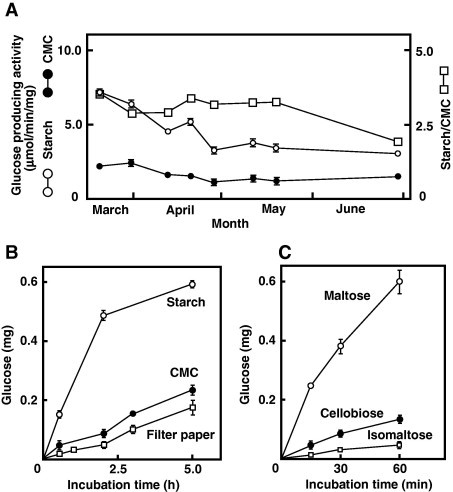
Seasonal changes in the glucose-producing activities from starch and carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) in the digestive fluid of Aplysia kurodai. (A) Gastric digestive fluid was collected from ten A. kurodai on March 9 and 30; April 13, 20 and 28; May 11 and 18; and June 30 in 2013. Digestive fluids from three to four sea hare were combined and the enzyme activities in the three groups of digestive fluid were assayed. The digestive fluid (5 μl) was incubated in 0.2 ml of 1% starch or 1% CMC in 50 mM acetate buffer, pH 5.5, at 37 °C for 10 min. The reaction was terminated by heat treatment (95 °C, 5 °min), and glucose liberated from starch and CMC was determined by the Glucose CII Test Wako kit using glucose oxidase. Glucose-producing activity and ratio of activity towards starch and CMC were calculated from at least three separate experiments. Comparison of the glucose-producing activities from starch, CMC, filter paper (B), and maltose, cellobiose, and isomaltose (C) in the digestive fluid of A. kurodai collected on March 23. One percent starch, CMC, maltose, cellobiose, and isomaltose (0.2 ml in 50-mM acetate buffer at pH 5.5) were incubated with 2 μl of the digestive fluid (collected on Apr 13), and liberated glucose was determined. Filter paper (50 mg) was incubated with 2 μl of the same digestive fluid. Enzyme activity (mean ± S.D.) was calculated from at least three separate determinations.
