Fig. 5.
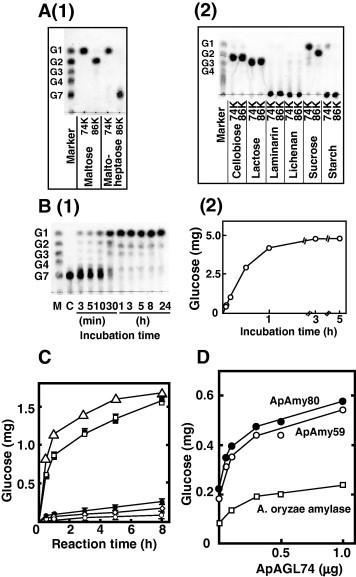
Comparison of the enzymatic properties of ApAGL74 and ApAGL86. (A-1) Maltose and maltoheptaose (0.2 ml, 1 mg/ml in 10 mM acetate, pH 6.0) were incubated with 0.03 U of ApAGL74 or ApAGL86 at 37 °C for 24 h. (A-2) Cellobiose, lactose, laminarin, lichenan, sucrose, and starch (0.2 ml, 10 mg/ml in 10 mM acetate, pH 6.0) were incubated with 0.03 U of ApAGL74 or ApAGL86 at 37 °C for 24 h. Reaction products were analyzed by TLC. (B-1) Time-course hydrolysis of maltoheptaose by ApAGL74. ApAGL74 (0.1 U) was incubated with celloheptaose (1.0 ml, 5 mg/ml in 10 mM acetate, pH 6.0) at 37 °C for the time indicated. The reaction products were analyzed by TLC (B-1) and glucose content was determined by the Glucose CII Test Wako (B-2). (C) Hydrolysis of starch by the synergistic action of amylase and α-glucosidase. Incubation of 0.08 U of ApAmy59 and ApAmy80 with starch (1.0 ml, 2 mg/ml in 50 mM acetate, pH 5.5 containing 10 mM CaCl2) in the absence or presence of ApAGL74 (0.08 U) at 37 °C for the time indicated. Glucose (mean ± S.D.) was determined by at least three separate experiments. ApAmy59 (opened circles), ApAmy80 (closed circles), ApAGL74 (open diamonds), ApAmy59 + ApAGL74 (opened squares), ApAmy80 + ApAGL74 (closed squares), and ApAmy59 + ApAmy80 + ApAGL74 (opened triangles). (D) Hydrolysis of sea lettuce by the synergistic action of amylase and α-glucosidase. Sea lettuce (1.0 ml, 20 mg/ml in 50 mM acetate containing 10 mM CaCl2) was incubated with 0.1 U of ApAmy59 and ApAmy80 in the absence and presence of ApAGL74 at 37 °C for 24 h. Aspergillus amylase was incubated in the absence of CaCl2. Glucose (mean) was determined by two separate experiments.
