Figure 1.
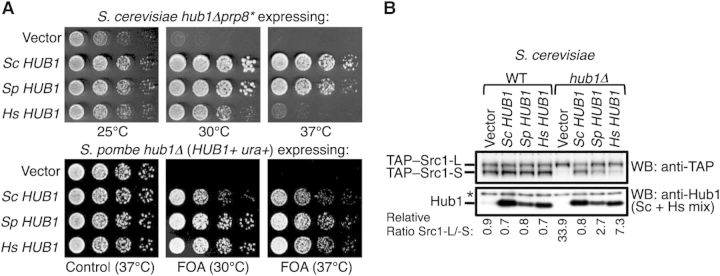
Conserved and divergent properties of Hub1. (A) Genetic complementation assays. Rescue of synthetic sickness of hub1Δprp8* in S. cerevisiae (top panel) and lethality of hub1Δ in S. pombe (bottom panel), by expression of Hub1-encoding genes (or cDNAs) from S. cerevisiae (Sc), S. pombe (Sp), and H. sapiens (Hs). For complementation in S. pombe, a URA4-bearing plasmid expressing WT SpHUB1 was shuffled-out from the hub1Δ strain by counter-selection with FOA. Growth assays with 5-fold serial dilutions on control or FOA-containing plates at indicated temperature are shown. (B) Complementation of altered alternative splicing of S. cerevisiae SRC1 in hub1Δprp8* cells by HUB1 orthologs at 30°C (like in A). Protein expression levels of TAP-tagged Src1-L and Src1-S isoforms as well as Hub1 were monitored by immunoblotting using anti-TAP and anti-Hub1 antibodies, as described previously (Mishra et al., 2011). The quantification of the relative ratio between Src1-L and Src1-S isoforms is given below.
