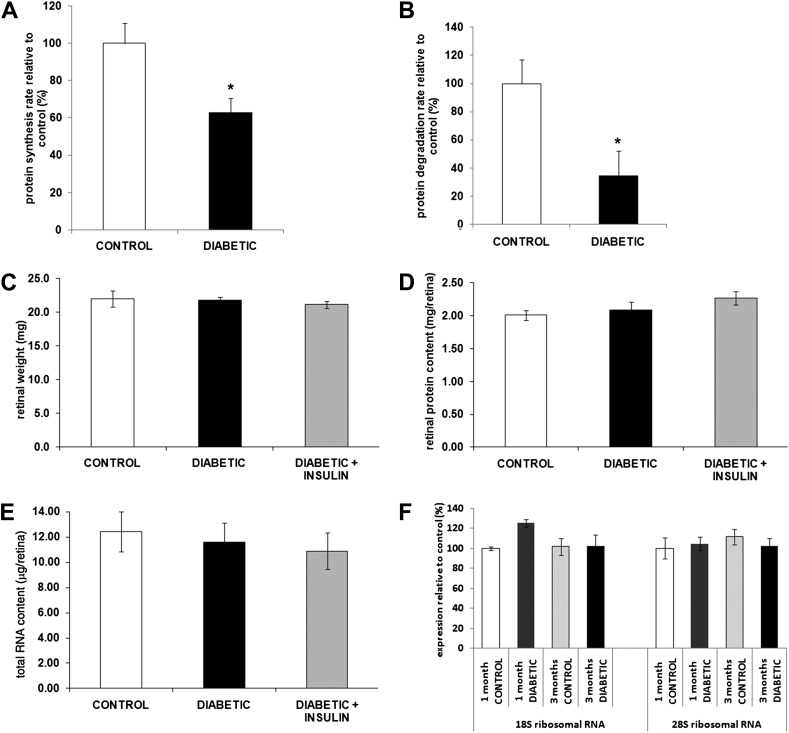
Figure 2.
Diabetes reduces retinal protein synthesis and degradation independent of retinal weight, total protein, total RNA, and ribosomal RNA content. Retinas from 3-month diabetic STZ rats treated or not with systemic insulin and age-matched controls were harvested for assessment of the impact of diabetes on retinal protein synthesis (A), degradation rate (B), and composition (C–F). Diabetes reduced retinal protein synthesis (A) and retinal degradation (B) as measured by the pulse-chase method without affecting retinal wet weight (C), protein content (D), total RNA content (E), and ribosomal RNA content (F) (n ≥ 20/group). *Significantly different from control.