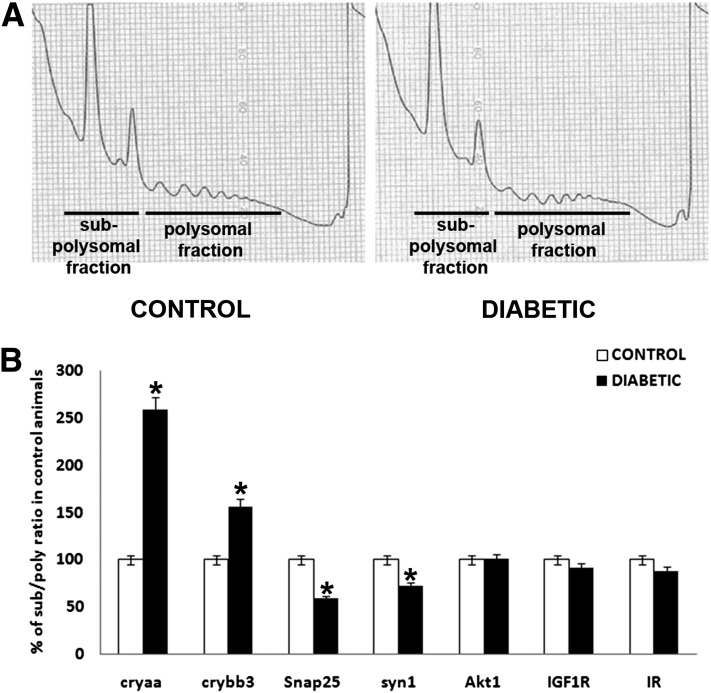
Figure 3.
Diabetes reduces retinal protein synthesis through an impairment in both peptide chain initiation and elongation while affecting specific mRNA translation rates. The impact of diabetes on polysome profiles and RNA pools of the subpolysomal and polysomal fractions was also analyzed. Representative polysome profiles are presented and show that translation efficiency is due to impairment in both peptide chain initiation and elongation in the retina during diabetes (A). RNA isolated from both subpolysomal and polysomal fractions was analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR and demonstrated the decreased translation of α-A-crystallin (cryaa) and β-B3-crystallin (crybb3) mRNA and increased translation of synaptic genes Snap25 and synapsin 1 (syn1) during diabetes (B). *Significantly different from control.