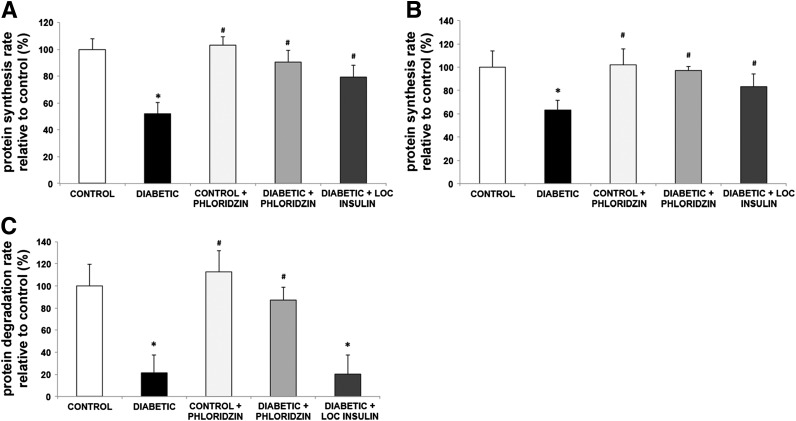
Figure 4.
Blood glucose normalization reverses both retinal protein synthesis and retinal protein degradation induced by diabetes, whereas local insulin only reverses the reduction in protein synthesis. Rats with 3 months of diabetes were treated by administration of phloridzin twice daily or insulin subconjunctivally once daily for the last 4 days. Protein synthesis rate was then measured using the flooding dose of phenylalanine method, and results show that both treatments partially reverse the protein synthesis decrease induced by diabetes (A). Similarly, retinas from diabetic and age-matched control rats treated with either phloridzin twice daily or insulin subconjunctivally once daily for the last 4 days were harvested and incubated ex vivo with radiolabeled methionine to measure protein synthesis rate (B) followed by pulse-chase method to measure protein degradation rate (C). Phloridzin treatment for 4 days reversed both protein synthesis and protein degradation rates, whereas ocular insulin only reversed the protein synthesis defects induced by diabetes (n ≥ 8/group). *Significantly different from control (P < 0.05). #Significantly different from diabetic (P < 0.05). LOC, local.