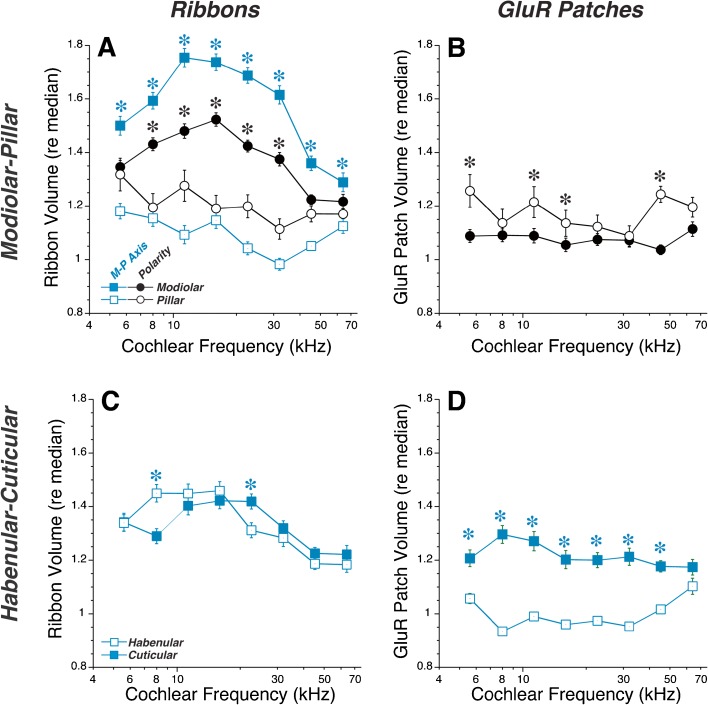
FIG. 6.
Complementary gradients are also seen in relative sizes of ribbon and GluR patches in control ears in which interspecimen differences in staining intensity required that sizes be normalized. The criteria for distinguishing modiolar versus pillar and habenular versus cuticular synapses are as described in Fig. 5. Techniques for normalizing ribbon and GluR-patch volumes are as described in Fig. 4, and the underlying database is the same as that used for Fig. 4. Group means (±SEMs) are shown in all panels. Keys in A, C also apply to B, D, respectively. Asterisks indicate that group differences are significant at the P < 0.01 level by a two-tailed t test.