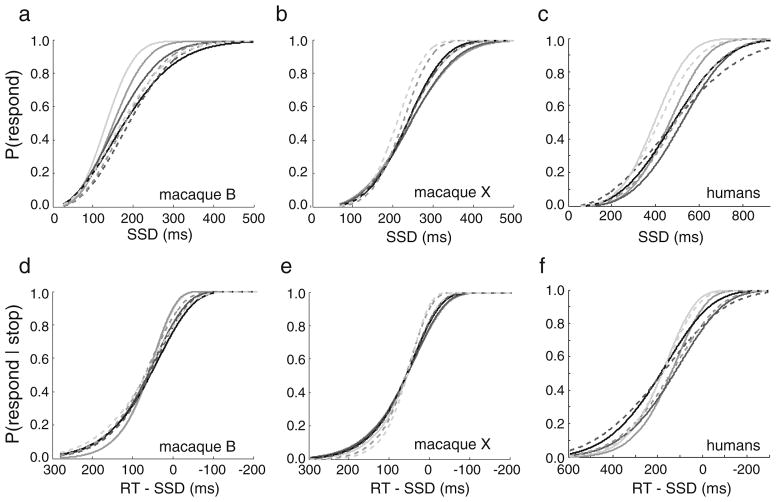
Fig. 5.
Response inhibition performance within each signal strength level for (a, d) macaque B, (b, e) macaque X, and (c, f) humans. (a–c) Probabilities of responding during stop trials as a function of stop signal delay (SSD). (d–f) Transformed inhibition functions, plotted as the probability of responding during stop trials as a function of the mean no-stop response time (RT) minus SSD. Fitted Weibull functions are shown. Solid gray lines depict right-target color percentages under 50%, and dashed gray lines depict percentages over 50%, with darker colors denoting percentages closer to 50%. The solid black lines depict the 50% right-target color percentage