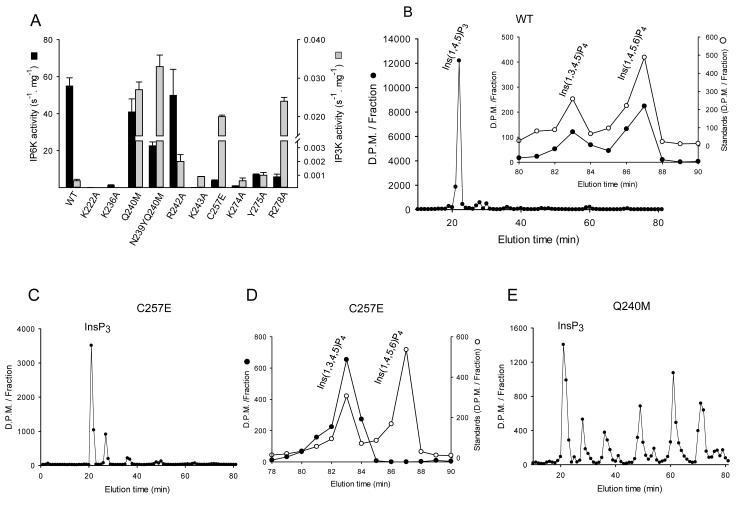
Fig. 6. HPLC analysis of the kinase activities of wild-type and mutant IP6Ks.
A, InsP6 kinase (black bars) and Ins(1,4,5)P3 kinase (grey bars) activities of wild-type HsIP6K2 and the indicated mutants (means ± standard errors, n ≥3). Panels B shows representative HPLC analysis (Partisphere SAX; Gradient 2) of Ins(1,4,5)P3 kinase activities of wild-type HsIP6K2 (8 μg, 7 hr). The inset to panel B shows HPLC analysis (Q100 SAX; Gradient 3) of the InsP4 products formed by the wild-type enzyme (closed circles) together with the elution of internal standards of [14C]-Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 and [14C]-Ins(1,4,5,6)P4 (open circles). Panel C shows a representative HPLC analysis (Partisphere SAX; Gradient 2) of Ins(1,4,5)P3 kinase activity of a Cys257Glu mutant of HsIP6K2 (5 μg, 1 hr). Panel D shows a representative HPLC analysis (Q100 SAX; Gradient 3) of the InsP4 products formed by a Cys257Glu mutant of HsIP6K2 (5 μg, 45 min). Panel E shows a representative HPLC analysis of Ins(1,4,5)P3 kinase activity of a Gln240Met mutant of HsIP6K2 (11 μg, 7 hr).