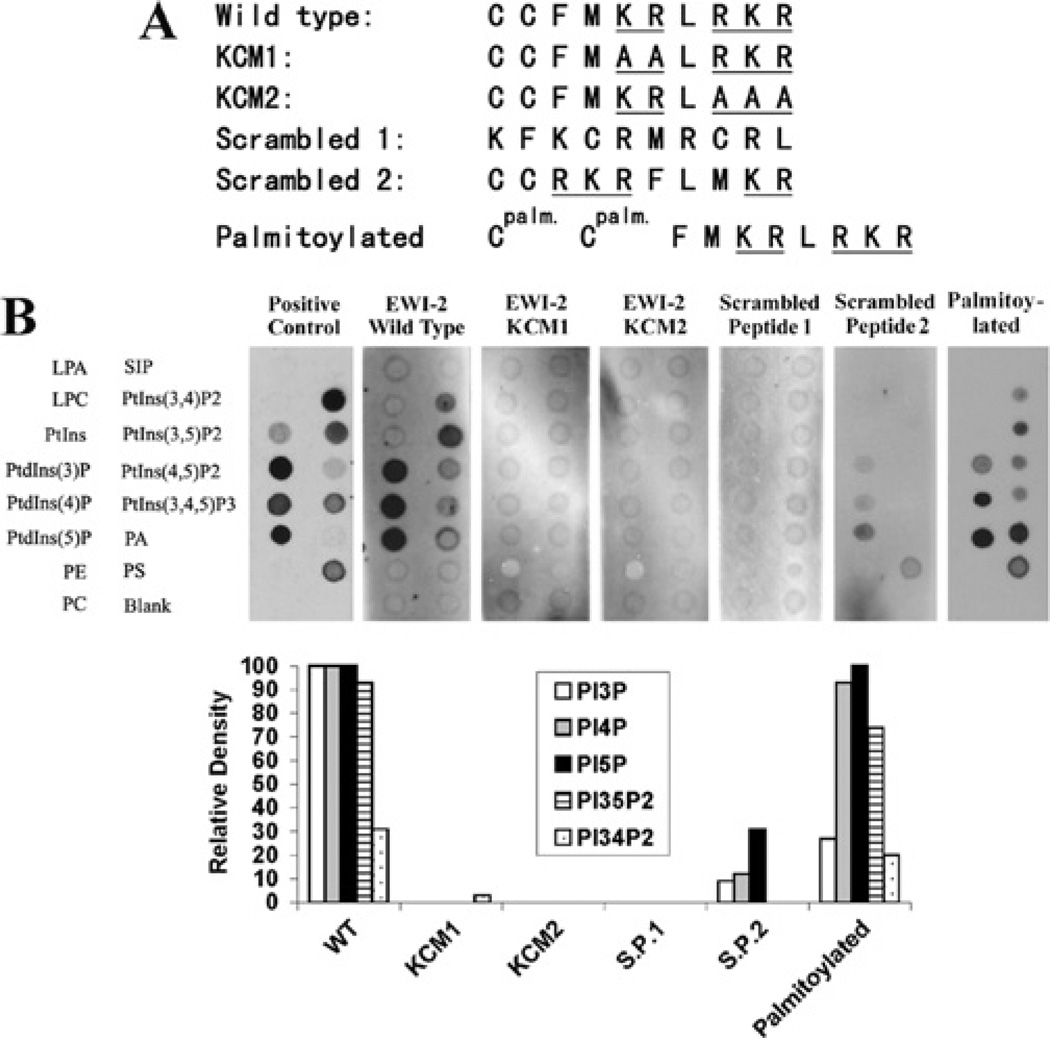
Figure 2. The basic residues in the EWI2 cytoplasmic domain determine PIP interaction.
(A) Peptide sequences of the EWI2 wild-type and mutated cytoplasmic domains are listed. In KCM1 and KCM2 mutated peptides, the two clusters of basic residues were replaced either individually or simultaneously by alanine residues, and the mutant peptides were designated as labelled. (B) All peptides were labelled with biotin at the N-termini, and the palmitoylated peptide contained a palmitate group on each cysteine residues (see the Materials and methods section). After being incubated with the peptides, the PIP strips were blotted with HRP-conjugated avidin and the bindings were visualized with chemiluminescence. The positive control is the GST-LL5-α PH domain. The densities of dots were quantified as described in Figure 1(B). LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; LPC, lysophosphocholine; PA, phosphatidic acid; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PS, phosphatidylserine; S1P, sphingosine 1-phosphate.