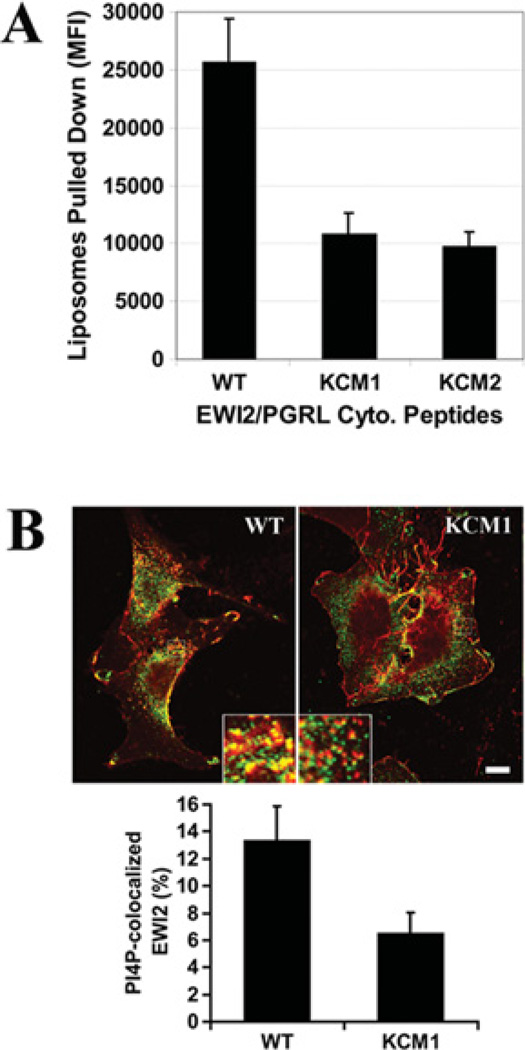
Figure 3. Interaction of the EWI2 cytoplasmic domain with membrane PIPs.
(A) The binding of the EWI2 tail to PI4P in liposomes. The fluorescent liposomes that contain POPC, PtdIns4P and NBD PC at amolar ratio of 53:1:6were incubated with the avidin-conjugated agarose beads that were immobilized with biotinylated EWI2 cytoplasmic domain peptides in vesicle-binding buffer at room temperature for 1 h. The beads were then collected with brief centrifugation, followed by three washes with vesicle-binding buffer. The fluorescence intensity of the liposomes that were pulled-down by the beads was measured at an excitation wavelength of 485 nm and an emission wavelength of 535 nm using a HTS7000 Fluoremeter (PerkinElmer). The results (means ± S.E.M.) for four independent experiments were plotted as a histogram; the differences between the wild-type and KCM1 and KCM2 peptides are statistically significant (P < 0.01). (B) The intracellular co-localization of EWI2 with PtdIns4P. NIH 3T3 transfectant cells were fixed, permeabilized and incubated with anti-EWI2 mAb, anti-PIP4 mAb and secondary antibodies as described in the Materials and methods section. Confocal microscopic images in the same Z plane were captured under the identical instrument setting. Scale bar, 10 µM. The co-localization of EWI2 (red) with PtdIns4P (green) was quantified using Zeiss LSM 510 software with a threshold of 170 set for both green and red channels. The PtdIns4P -co-localized EWI2 was presented as Manders co-localization coefficient X 100% and projected as the means ± S.E. (n = 3). In each experiment, more than 70 cells were analysed from each transfectant. P < 0.05 between wild-type and KCM1 transfectant cells.