Figure 1. Schematic diagram of proSAAS and proSAAS-derived peptides.
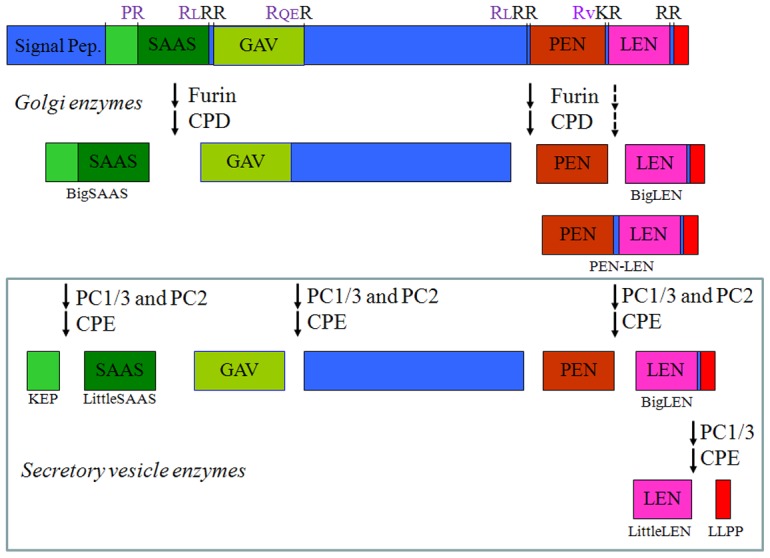
The major peptides derived from proSAAS are indicated, along with the enzymes involved in the cleavages. The amino acids within the cleavage site are shown (top row); residues in black are removed by the carboxypeptidase (CPD or CPE), and residues in purple remain on the C-terminus of the upstream peptide. The sites that are efficiently cleaved by furin/CPD are indicated by solid arrows; these cleavages generate big SAAS, an intermediate peptide representing GAV and the mid-portion of proSAAS, and PEN-LEN. Furin can also cleave PEN-LEN into PEN and big LEN (dashed arrow) but this cleavage does not go to completion in mouse brain. Within secretory vesicles, big SAAS is cleaved into KEP and little SAAS, the middle portion of proSAAS is cleaved into GAV and an un-named peptide, PEN-LEN is cleaved into PEN and big LEN, and big LEN is converted into little LEN and a 4-residue peptide LLPP. The conversion of big LEN into little LEN and LLPP is primarily catalyzed by PC1/3 and CPE. In addition to these major forms of the proSAAS-derived peptides, smaller forms of little SAAS, GAV, and PEN are present in mouse brain although the levels of these truncated peptides are generally lower than the levels of the peptides indicated in this figure.
