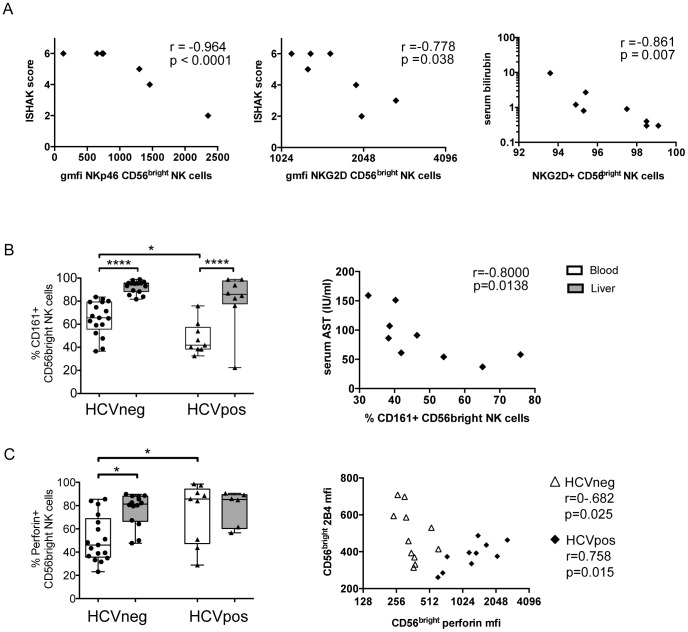
Figure 4. Unique liver and blood NK phenotypes associate with markers of disease progression.
Correlative analysis of NK cell immunophenotype and function in the liver and blood with clinical measures of HCV infection such as ISHAK score, ALT, AST, serum bilirubin, HCV RNA and INR were performed. The significant associations of liver NK cell receptors with clinical markers are displayed (A) along with correlations between the frequency of CD161+, (B) and perforin expression on blood CD56bright NK cells (C) with clinical markers and the expression of other NK cell receptors. Correlations were done using Spearman's rank test and statistical significance was accepted at p<0.05 and is indicated by * (p<0.05), ** (p<0.01) and *** (p<0.001).