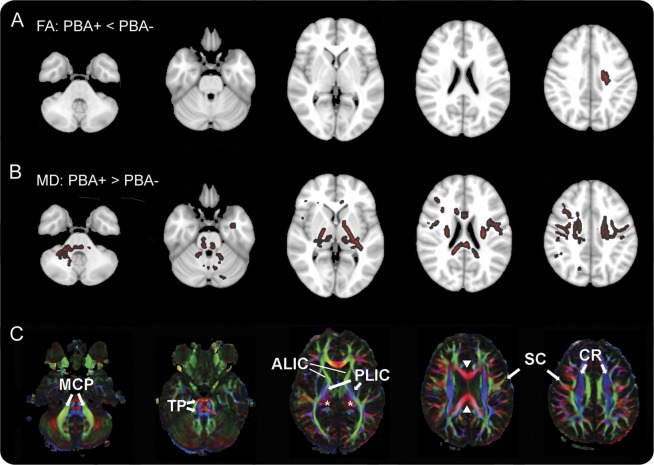
Figure 3. Differences in diffusion tensor imaging between patients with and without pseudobulbar affect.
(A, B) Color indicates white matter regions where diffusion properties differ between patients with pseudobulbar affect (PBA+) and patients without pseudobulbar affect (PBA−) (tract-based spatial statistics, threshold-free cluster enhancement, p < 0.05). (C) Directionally encoded color map providing labels for selected structures. (A) Fractional anisotropy (FA) was reduced in PBA+ patients only in a small region underlying the left motor cortex. (B) Mean diffusivity (MD) was greater in PBA+ patients in multiple white matter areas, including the middle cerebellar peduncles (MCP), transverse pontine fibers (TP), bilateral posterior limbs of the internal capsule (PLIC), left anterior limb of the internal capsule (ALIC), thalamus (asterisks), frontotemporal subcortical white matter, corona radiata (CR), white matter underlying the motor cortex (SC), and corpus callosum (solid arrowheads). Axial sections are shown in radiologic convention with right brain on the left side.