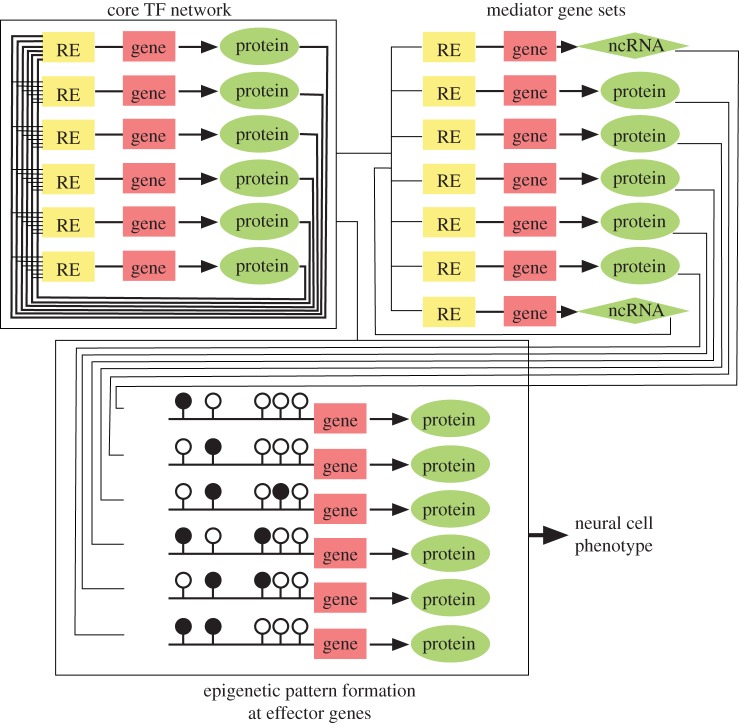
Figure 1.
Core networks and their predominant effects on effector genes in neural cells. Open and filled lollipops denote unmethylated and methylated CpG sites, respectively. In the central nervous system, TFs such as SOX2, NEUROG1 and ASCL1 direct formation of the robust network of neural cells. The TF network controls the expression of mediator and effector gene sets, thereby establishing the neural cell functions. Note that fluctuations in the core gene network can be amplified through these pathways, resulting in the generation of epigenetic variations such as those frequently seen after TF-based reprogramming.