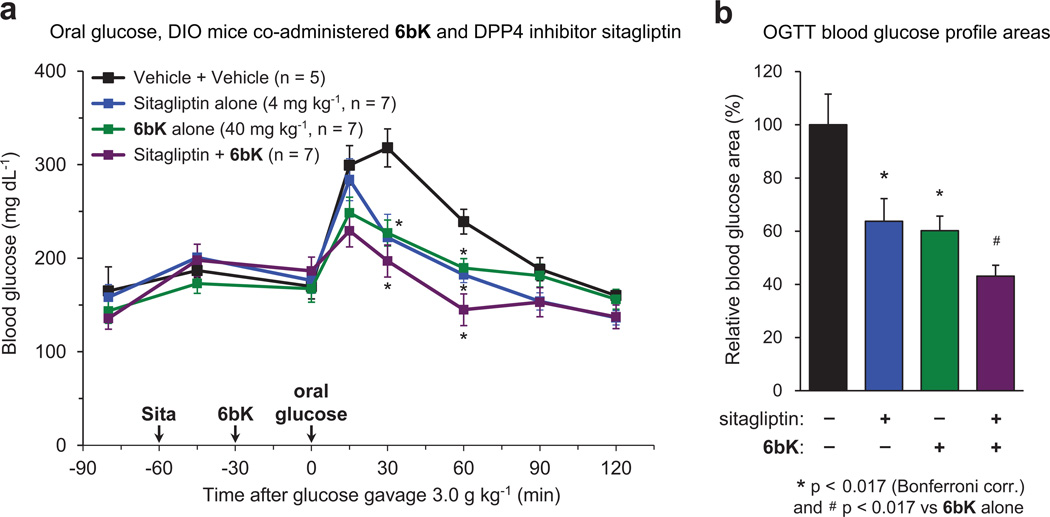
Extended Data Figure 8. Effects of co-administration of 6bK and dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) inhibitor sitagliptin followed by oral glucose challenge.
a, DIO mice were first treated with either oral gavage of sitagliptin (4 mg kg−1, 5 ml kg−1 in sterile saline, n = 14) or saline alone (n = 12). After 30 min, each group of mice were treated either with a low dose of 6bK (40 mg kg−1, n = 7) or vehicle alone (n = 5), and after an additional 30 min all mice were given a bolus of glucose by gavage (3.0 g kg−1, 10 ml kg−1). Mice treated with the combination of sitagliptin and 6bK displayed glucose levels lower than baseline (t = 0) after 60 min. b, Blood glucose profile areas of sitagliptin and 6bk were similarly reduced by 60–64% compared to vehicle alone, and further 15% lower when sitagliptin and 6bK were co-administered. Symbol and bar colour-coding: black, vehicle alone; blue, sitagliptin alone; green, 6bK alone; purple, sitagliptin + 6bK. All data points and error bars represent mean ± s.e.m. Statistics were performed using a one-tail Student’s t-test. Significance levels shown in the figures are: *P < 0.017 (Bonferroni correction) versus vehicle control group, #P < 0.017 versus the 6bK cohort. See Supplementary Methods for a description of the AUC calculation. The data shown are from a study performed once.