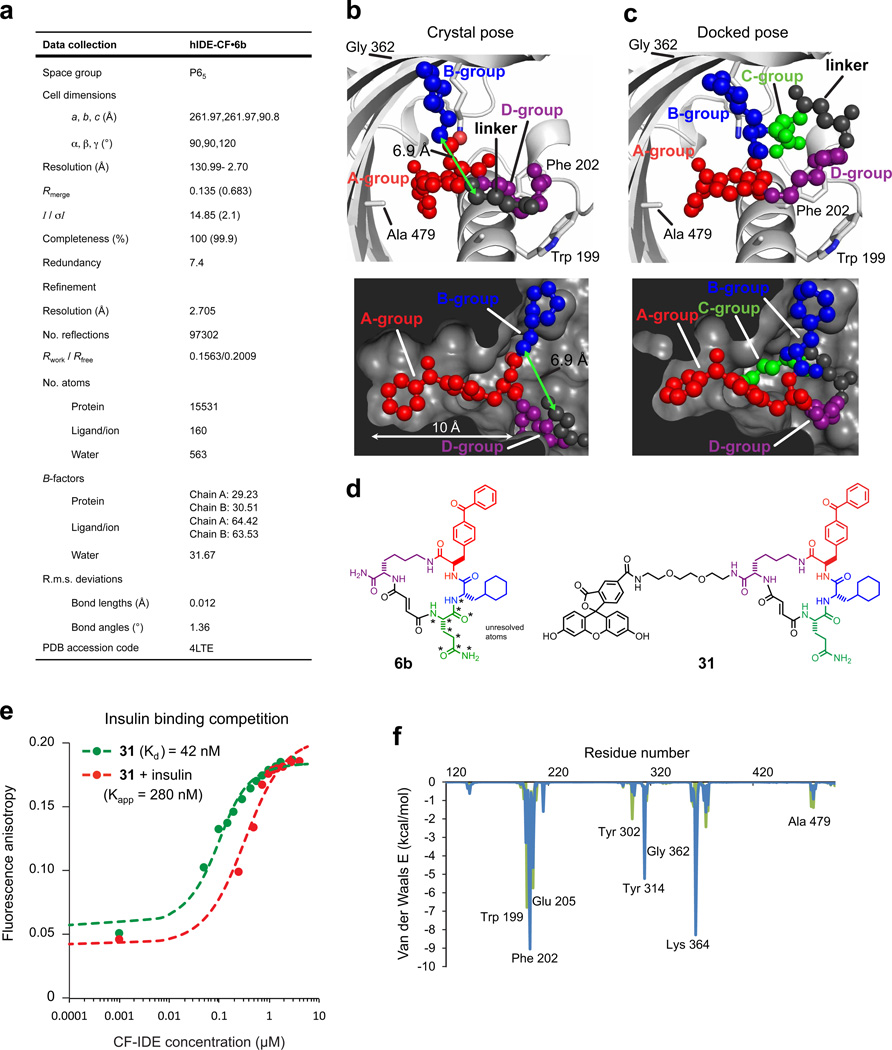
Extended Data Figure 3. Data collection and refinement statistics (molecular replacement), docking simulation for 6b, and competition test between insulin and fluorescein-labelled macrocycle 31 for binding cysteine-free IDE (CF-IDE).
a, One crystal was used to solve the CF-IDE•6b structure. The highest-resolution shell is shown in parentheses. Structure coordinates are deposited in the Protein Data Bank (accession number 4 LTE). b, Molecular docking simulations are consistent with the placement of building blocks A and B in the structural model (two views shown: top and bottom panels). The structure of 6b in the binding site from crystallographic data with composite omit map contoured at 1.0 σ (p-benzoyl-phenylalanine is shown in red, the cyclohexylalanine in blue, the fumarate linker in grey, and the d-lysine backbone in purple). c, Highest-scoring pose from DOCK simulations (glutamine group is shown in green, see Supplementary Information for docking calculations). d, Structure of macrocycle 6b and fluorescent analogue 31. Stars indicate atoms not resolved in the crystal structure (the Gln building block and four atoms of the flexible macrocycle backbone). e, Competition test between the fluorescein-labelled macrocycle 31 and insulin for binding CF-IDE. Cysteine-free catalytically inactive IDE was titrated against 0.9 nM macrocycle 31 alone (filled green circles) or together with 2.15 µM insulin (red filled circles), producing a shift in apparent dissociation constant for macrocycle 31 according to equation (1) (Supplementary Information). f, Residue-decomposed energy of the crystal (green) and docked (blue) poses of 6b (see Supplementary Information for docking calculations).