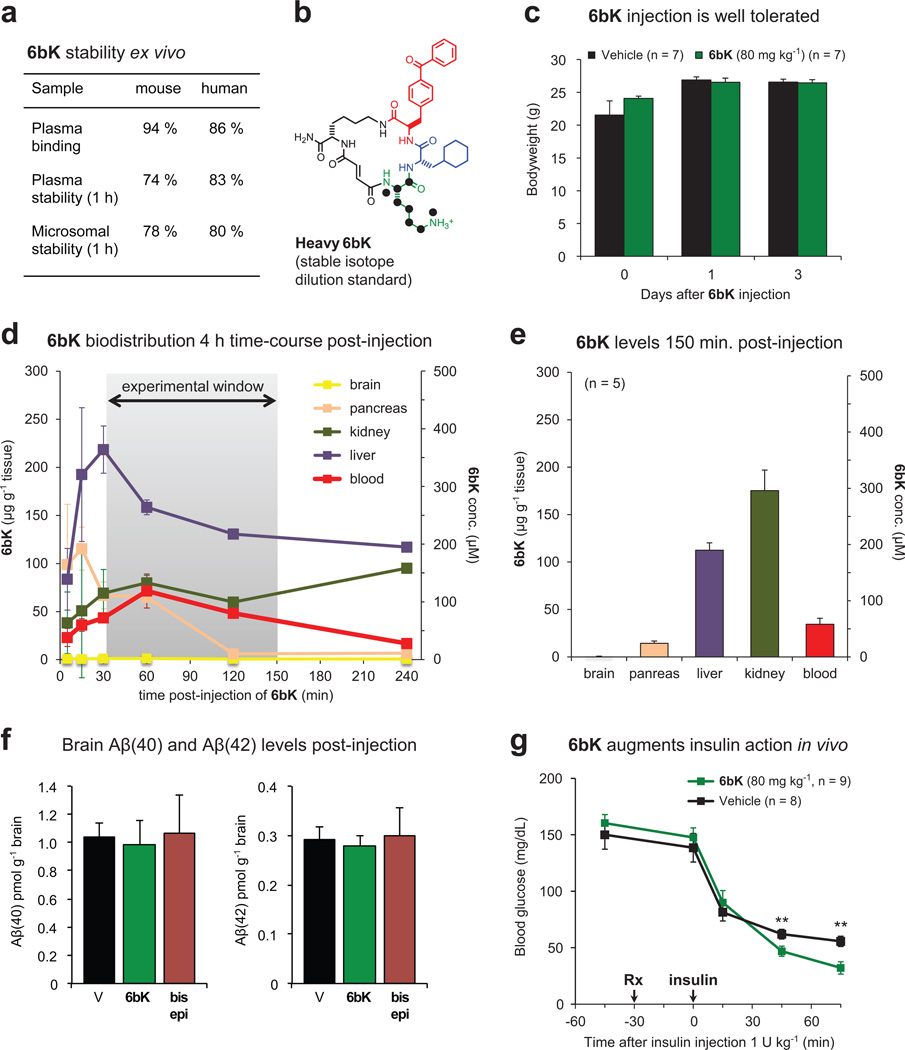
Extended Data Figure 5. Pharmacokinetic parameters of 6bK, augmented insulin hypoglycaemic action by 6bK in mice, and effects of 6bK on amyloid peptide levels.
a, Plasma binding, plasma stability, and microsomal stability (1 h incubation) data (S. Johnston and C. Mosher, personal communication). b, Heavy-labelled 6bK was synthesized with 15N, 13C-lysine for stable-isotope dilution LC-MS quantitation. c, Behaviour and post-experiment body weight measurements were not affected for mice treated with 6bK (green; 80 mg kg−1) versus vehicle alone (black). The mice were active, and displayed normal posture, normal grooming and normal response to stimulation. d, Concentration of 6bK in mice tissues and plasma collected over 4 h determined by isotope dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS) with heavy-labelled analogue (n = 2 for all data except the last two time-points, for which n = 1). e, Average biodistribution of 6bK in five lean mice at 150 min post-injection of 6bK 80 mg kg−1 i.p. at the endpoint of an IPGTT experiment. We did not detect 6bK in the brain even using tenfold concentrated samples for LC-MS injection compared to other tissues. f, Treatment of C57BL/6J lean mice with 6bK (green, 80 mg kg−1, n = 6) does not change brain levels of Aβ(40) or Aβ(42) peptides in the brain 2 h post injection compared to treatment with vehicle alone (black, n = 5) or inactive diastereomer bisepi-6bK (brown, 80 mg kg−1, n = 6). g, Mice treated with a single injection of 6bK (green, 80 mg kg−1 i.p.) display increased hypoglycaemic response to insulin injection (Humulin-R, 1.0 U kg−1 i.p., see also Fig. 3b). Data shown in c–e and g are representative of two or more independent studies.