Figure 2.
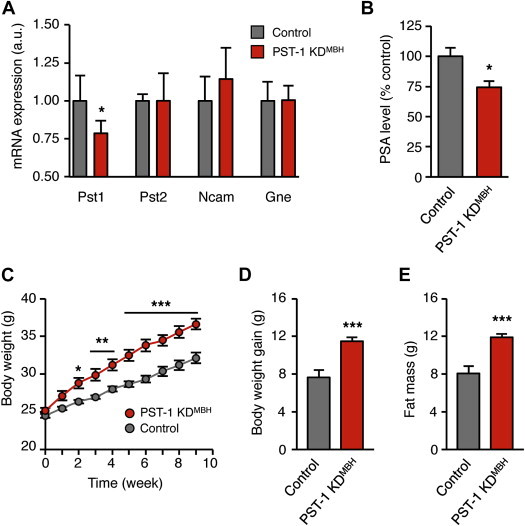
Reduction of polysialylation in the hypothalamus increases the body weight gain on HFD. St8sia4 knockdown mice, designated as PST-1 KDMBH mice, were stereotactically injected in the mediobasal hypothalamus with ∼7.5 × 105 shRNA-expressing lentiviral vectors against a Pst1 sequence. Control mice received lentiviral vectors targeting a non-mammalian sequence. (A) Effect of the lentiviral vectors-mediated RNA interference on relative mRNA expression of genes involved in the PSA signaling, assessed by RT-qPCR on mediobasal hypothalamus extracts from standard diet-fed mice (n = 4 control; n = 5 PST-1 KDMBH; *: p < 0.05; unpaired t test. (B) PSA level in the mediobasal hypothalamus of PST-1 KDMBH mice fed a HFD for 2 months, compared to control mice (n = 9 control; n = 9 PST-1 KDMBH; *: p < 0.05; unpaired t test). (C) Kinetic of the body weight of PST-1 KDMBH and control mice during 2-month HFD (*: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01. ***: p < 0.001; two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post-hoc test). (D) Body weight gain of PST-1 KDMBH and control mice after 2-month HFD (***: p < 0.001; unpaired t test). (E) Fat mass of PST-1 KDMBH and control mice after 2 month-HFD (***: p < 0.001; unpaired t test). All results are mean ± SEM.
