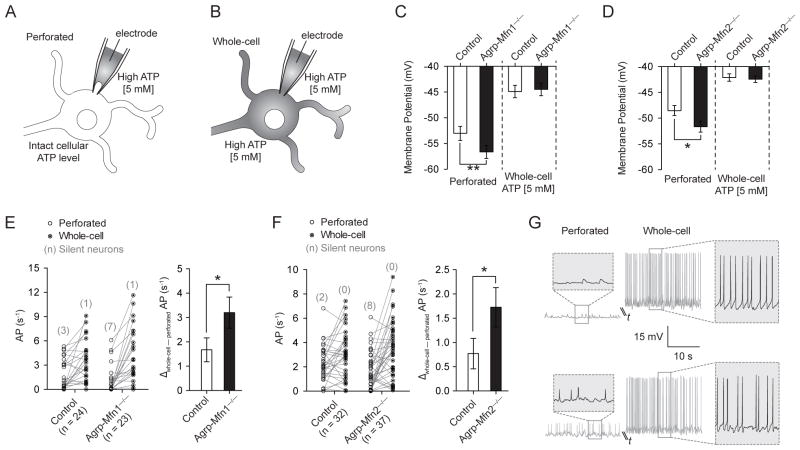
Figure 6. Intracellular ATP levels determine electrical differences in Agrp-Mfn1−/− and Agrp-Mfn2−/− neurons.
(A) Schematic illustration showing patch clamp recording utilizing perforated clamp with high ATP (5 mM) in the pipette solution or (B) traditional whole-cell recording after patch membrane rupture. (C) Membrane potential in control and Agrp-Mfn1−/− neurons during perforated and whole-cell recordings. (D) Similar to (C), data represent recordings from control and Agrp-Mfn2−/− neurons. (E) Firing rate of control and Agrp-Mfn1−/− cells during perforated clamp and after patch rupture. Number of silent neurons is represented in parenthesis. (F) Similar to (E), data represent recordings from control and Agrp-Mfn2−/− neurons. (G) Two representative traces to illustrate the electrical responses of Agrp neurons during perforated and whole-cell recordings. The cell on the top is silent during perforated clamp, and becomes highly active after successful membrane rupture and whole-cell recording. Bars represent mean ± SEM. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01.