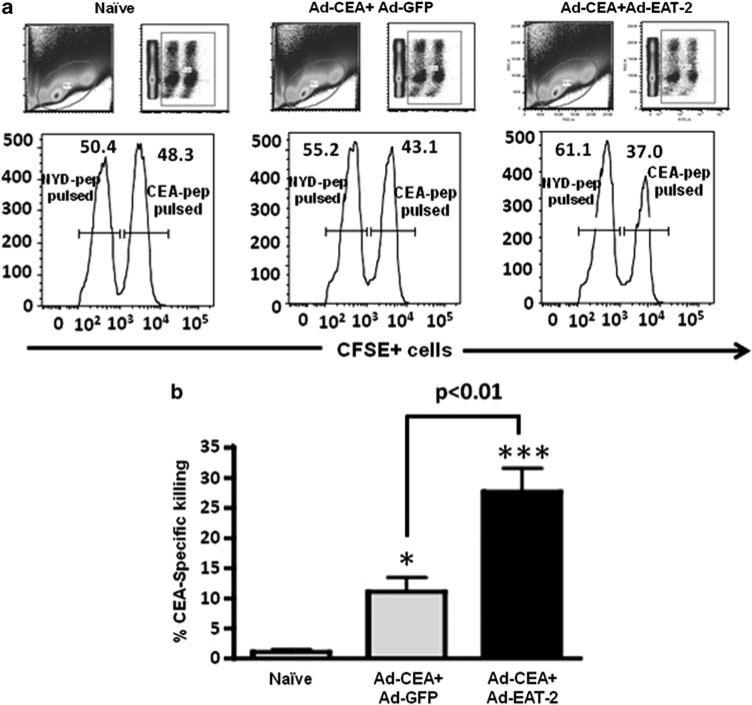
Figure 6.
Increased in vivo cytolytic activity of the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)-specific T cells in recombinant Ad5 vector (rAd5)-CEA and rAd5-Ewing's sarcoma's-activated transcript 2 (EAT2) co-immunized mice. C57BL/6 (n = 6) mice were co-immunized with equivalent viral particles (VPs) of rAd5-CEA mixed with either rAd5-EAT2 or rAd5-GFP (1 × 109 total vps). At 14 dpi, syngeneic splenocytes were pulsed with either an irrelevant peptide (NYD-pep) and stained with 1 μm CFSELow or with CEA-specific peptides, and labeled with 10 μm (CFSEHigh). Twenty hours after adoptive transfer into either naive or co-immunized mice, splenocytes were collected using a LSRII flow cytometer. (a) Representative figures of the CTL analysis from naive or vaccinated mice are shown. (b) Analysis for percent CEA-specific killing is shown. % carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester (CFSE)-positive cells were quantified using FlowJo software. % specific killing = 1 – ((% CFSEHigh /% CFSELow)immunized/(%CFSEHigh /% CFSELow)non-immunized). * Denotes P<0.05, *** denotes P<0.001 statistically different from naive animals. Representative figure of two independent experiments is shown.