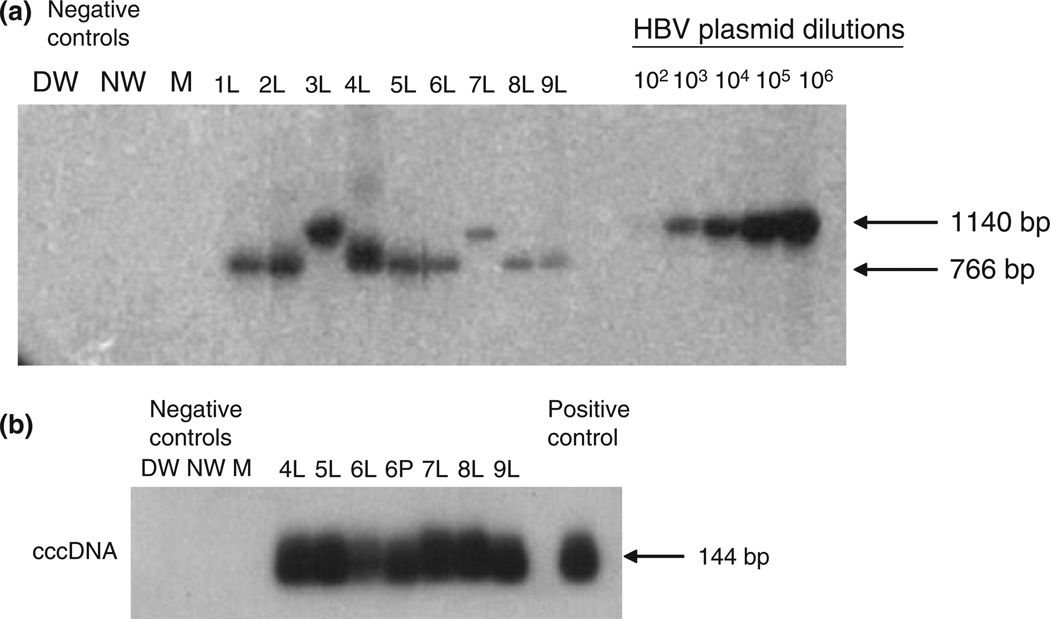
Fig. 1.
HBV genome detection in liver and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) collected from patients on suppressive anti-HBV therapy. (a) Detection of HBV P gene in explant liver (L) from nine patients (Cases 1–9). (b) Detection of HBV covalently closed circular DNA cccDNA in explant liver (L) and PBMC (P) from six patients (Cases 4–9). HBV DNA and cccDNA were detected using direct and nested PCR/nucleic acid hybridization (except in Cases 3 and 7 in which HBV DNA could be detected by a single round PCR). Serial dilutions of recombinant HBV DNA, used as a positive control, (102–106 virus genome equivalents, vge/mL) were simultaneously tested to determine approximate HBV viral load in liver samples by densitometry analysis. Negative controls included direct PCR water (DW), nested PCR water (NW), and a mock (M) extracted sample. The size of the expected direct (1140 bp) or nested (766 bp) DNA and cccDNA amplicons (144 bp) is indicated to the left of the figure.