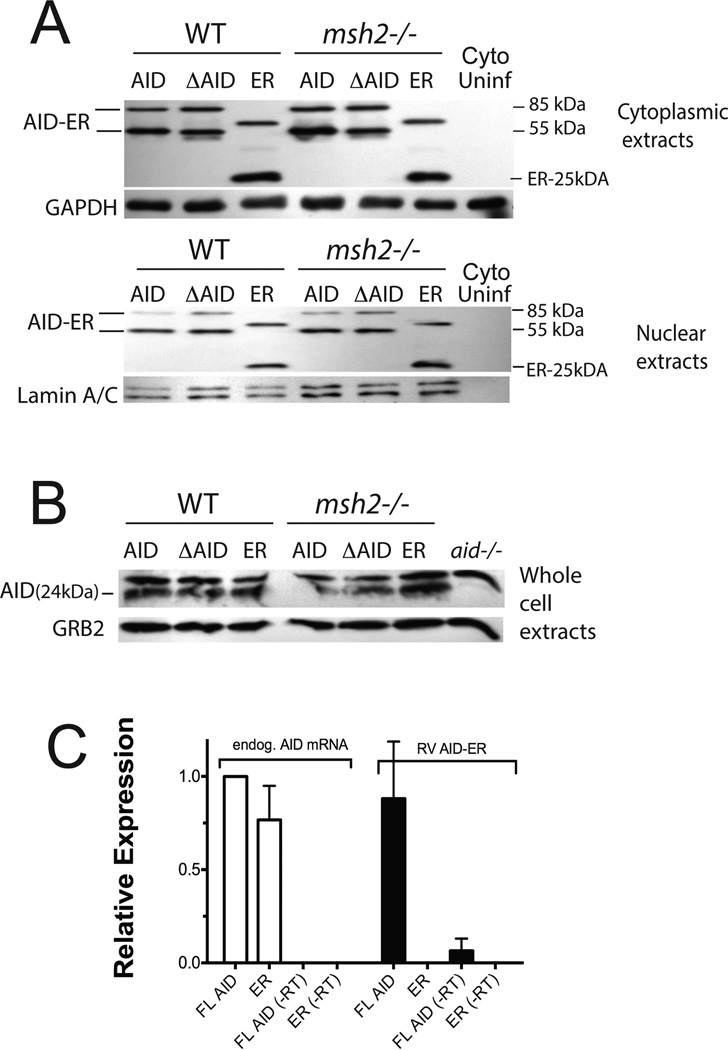
Figure 1. Quantitation of transduced AID-ER and endogenous AID levels in splenic B cells induced to switch to IgG3.
(A) Western blots of cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts (20 µg) from RV-infected splenic B cells one day after viral transduction were probed with anti-ER antibody, and with antibodies to GAPDH or Lamin A/C for loading controls. (B) Western blot of total cell extracts (75 µg) from the RV-infected or uninfected splenic B cells (from the same experiment shown in A) probed with antibody to mouse AID to detect endogenous AID. (C) qRT-PCR analysis shows that endogenous AID mRNA and AID mRNA transcribed from RV-AID-ER are present at similar levels in B cells activated to switch, one day after transduction with RV-AID-ER or RV-ER. Results of 2 independent experiments (2 mice) are normalized to endogenous AID mRNA in RV-AID-ER transduced cells. (−RT) indicates samples to which reverse transcriptase was not added.