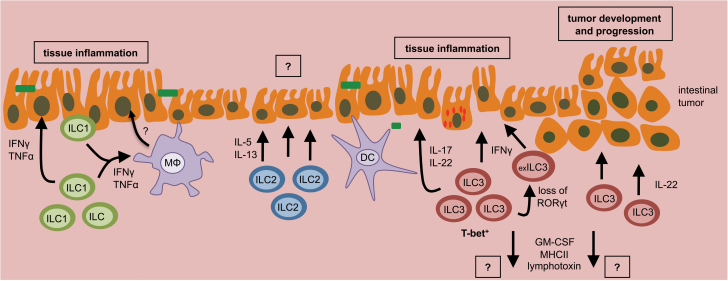
Fig. 2.
Dysregulated ILC responses can promote intestinal disease. Dysregulated ILC responses, or changes in the composition of ILC populations, can promote chronic intestinal inflammation or initiate the development and progression of intestinal tumors. This can occur through loss of regulation or sustained activation.