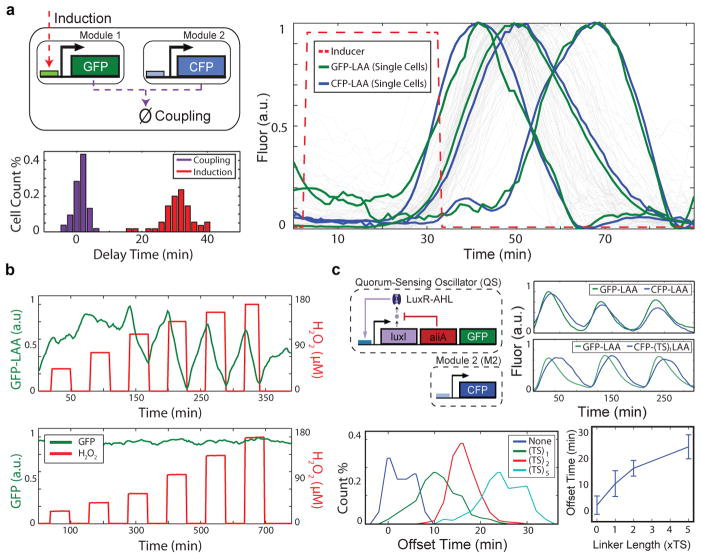
Fig. 1.
A rapid post-translational coupling platform based on shared degradation. (a) We measured the delays associated with module-module coordination by ClpXP (1±1 min) and input-output response via transcription/translation (31±5 min) in a single experiment by inducing the lux promoter and tracking the response of sfGFP-LAA (lux promoter) and CFP-LAA (Plac/ara-1promoter) in single cells (55 cell trajectories). (b) Rapid (< 2 min, our experimental timestep) induction of protein degradation by externally provided H2O2 produces reversible changes in ClpXP load in response to obstruction of RssB8, 9, 15. (c) To use post-translational coupling to drive downstream modules, we linked a quorum clock to a constitutively expressed fluorescent protein via the addition of identical LAA tags. With identical degradation tags, the constitutive module couples tightly to the quorum pacemaker. The addition of a variable-length linker (TS repeats) before the degradation tag phase-shifts the degradation dynamics, where longer linkers produced longer delays. The error bars indicate s.d. of offset time, centered at the mean (50–200 cells for each TS-linker length).