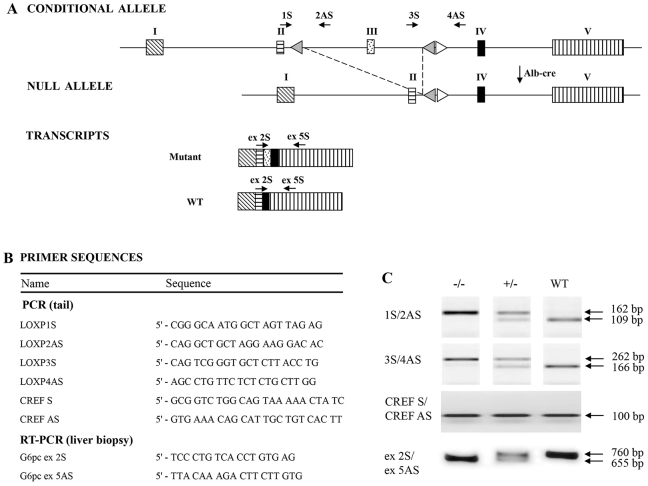
Fig. 1.
Generation of liver-specific G6pc-null mice. (A) Schematic representation of the G6pc conditional allele, the G6pc null allele, and the wild-type (WT) and mutant G6pc transcripts. Rectangles are exons; white triangles represent loxP sequences and gray triangles frt sequences. Arrows indicate the primers used to genotype the mice and verify exon 3 excision. (B) Name and sequence of the primers used for PCR on mouse tail DNA and RT-PCR on RNA extracted from liver biopsies. (C) PCR and RT-PCR analysis of WT and mutant alleles. The primer pair 1S/2AS is expected to amplify a fragment of 109 bp in the WT allele and a fragment of 162 bp in the mutant allele. The primer pair 3S/4AS is expected to amplify a fragment of 166 bp in the WT allele and a fragment of 262 bp in the mutant allele. The primer pair CREF S/CREF AS was used to detect a 100 bp Cre fragment. To verify liver-specific excision of exon 3, RT-PCR analysis was performed on RNA extracted from liver biopsy with the primer pair G6pc ex 2S/G6pc ex 5AS, expected to amplify a fragment of 760 bp in WT alleles and a fragment of 655 bp in the mutant allele. The images shown in the top two panels in C were selected from non-contiguous lanes of the same agarose gel and are representative of the results obtained.