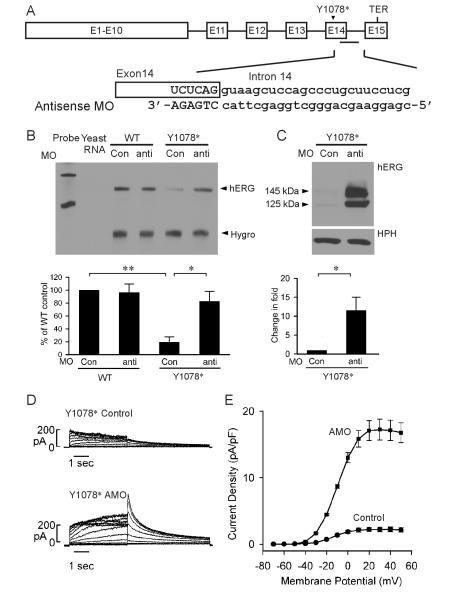
Fig. 6.
Inhibition of intron 14 splicing by antisense MO prevents NMD of Y1078*. Cells stably expressing the WT and Y1078* full-length splicing-competent hERG construct were treated with 5 μM invert (Con) or antisense MO for 48 hours. (A) Diagram of the full-length splicing-competent hERG construct and the sequences of antisense MO. (B) RPA analysis of the effect of antisense MO. RPA signals were quantified, normalized to hygromycin resistance gene (Hygro) and shown as percentage of WT control (n=3, **P<0.01, *P<0.05). (C) Immunoblot analysis of the effect of antisense MO. Cell lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-hERG and anti-HPH antibodies. The level of protein bands was quantified, normalized to HPH, and shown as fold changes in the presence of antisense MO (n=4). (D) Representative currents recorded from HEK293 cells stably expressing Y1078* following treatment with 5-μM invert (Control) or antisense MO (AMO) for 48 hours. (E) I-V plot of hERG tail current density measured at -50 mV following test voltages from -70 to 50 mV for WT and Y1078* in the presence of invert or antisense MO.