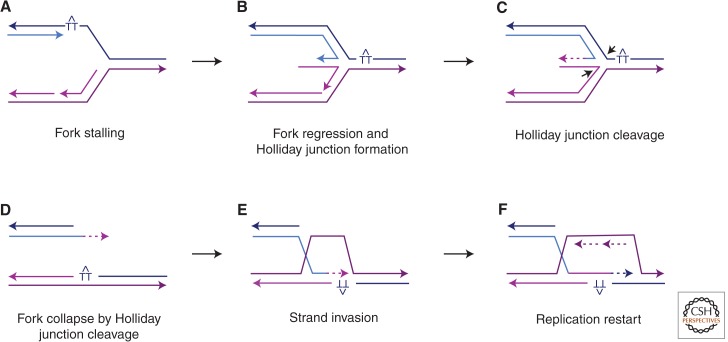
Figure 1.
Replication fork stalling and restart. DNA replication can be stalled at UV-induced thymidine dimers (TT), as well as DNA secondary structures. A stalled replication fork (A) can undergo regression and pairing of the newly synthesized strands to form a HJ “chicken foot” intermediate (B). The HJ can be cleaved by HJ resolvases (C) to lead to a collapsed fork, effectively a one-ended chromosome break (D). The free end can initiate HR by strand invasion (E) to bypass the lesion and resume replication (F). Newly synthesized DNA is depicted as dashed lines in the same color as the template; arrowheads indicate 3′ ends.