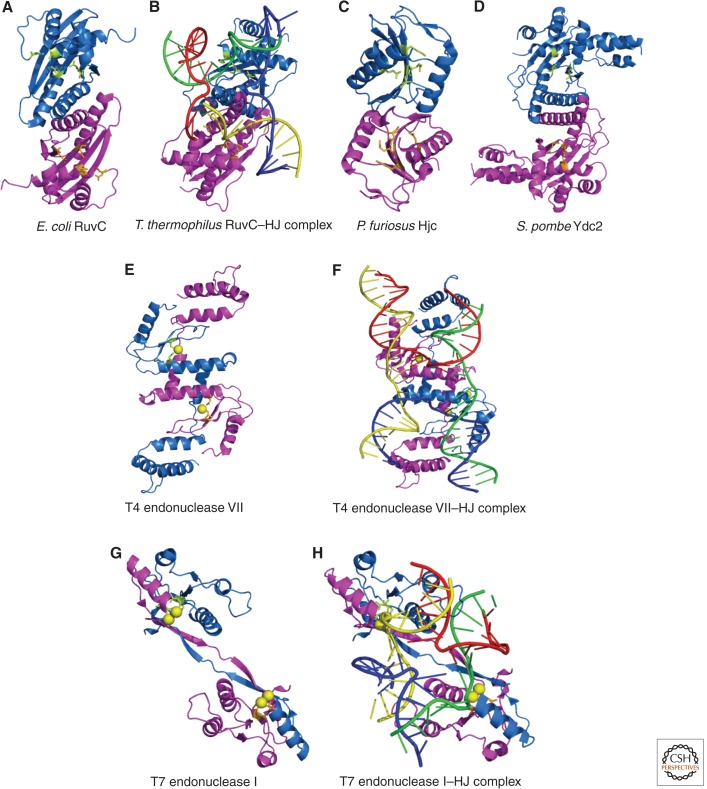
Figure 5.
Crystal structures of canonical Holliday junction resolvases. For each structure, the view is approximately down the dyad axis of the protein and looking toward the predicted DNA-binding surface. Each structure depicts two monomeric subunits, one colored in blue and the other in magenta. Active site residues are illustrated in ball and stick format and colored in lime and orange. Metal ions bound in the active site are shown as yellow spheres. For RuvC (A), T4 endonuclease VII (F), and T7 endonuclease I (G), the structures of the apoprotein and Holliday junction-bound enzyme are shown with the four DNA helices colored, as in Figure 2. The PDB IDs used to generate these structures are as follows: E. coli RuvC (A), 1hjr; T. thermophilus RuvC–HJ complex (B), 4ldo; P. furiosus Hjc (C), 1gef; S. pombe Ydc2 (D), 1kcf; T4 endonuclease VII (E), 1en7; T4 endonuclease VII–HJ complex (F), 2qnc; T7 endonuclease I (G), 1m0d; and T7 endonuclease I–HJ complex (H), 2pfj.