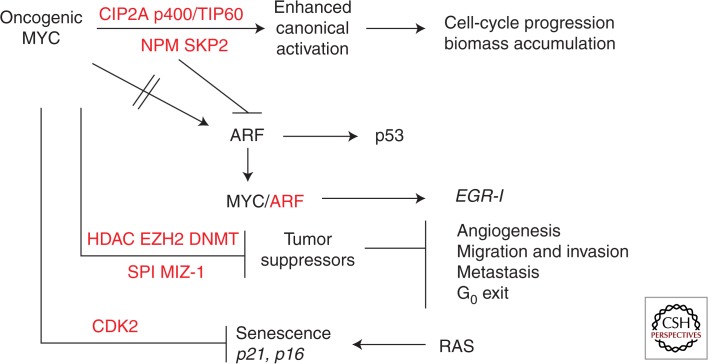
Figure 3.
Tumorigenesis pathways mediated by MYC and MYC cofactors. MYC-mediated tumorigenesis is primarily driven by enhanced canonical transactivation caused by overexpressed regulatory cofactors such as NPM, SKP2, and CIP2A and oncogenic MYC repression/silencing of tumor suppressors through cofactor complexes MIZ-1 and/or SP1 with HDACs, DNMTs, and EZH2. Loss of ARF and/or p53 and inhibition of RAS-induced senescence through CDK2 phosphorylation of MYC contributes to MYC-driven tumorigenesis. MYC cofactors are shown in red.