Figure 2. Within-Subject Classification Process.
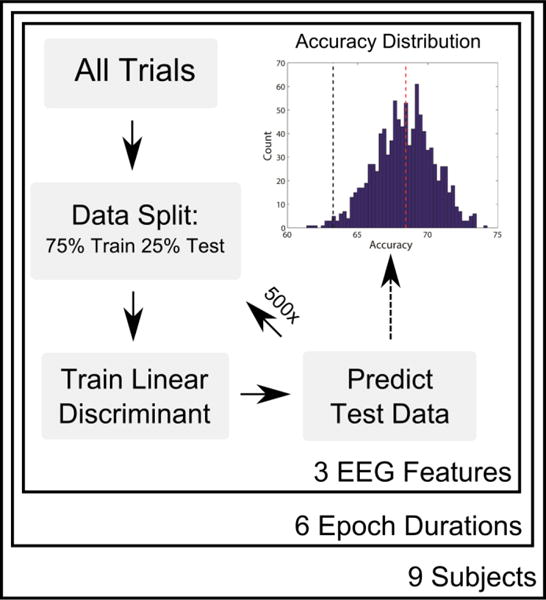
A graphical representation of the within-subject classification process. For a given subject, epoch duration, and EEG feature (cross-correlations, alpha power, or ASSRs), epochs are randomized into training and test sets. A linear discriminant is formed using the training data, and is then used to predict the side of attention for each epoch in the test set. The process is repeated 500 times, with new random splits of training and test epochs. The accuracies of all iterations form a distribution (upper right). The mean of the distribution (red dashed line) is reported as the overall classification performance, and the accuracy is stated to be significantly above chance if the 5/6th percentile of the distribution (black dashed line) is above 50%.
