Figure 1.
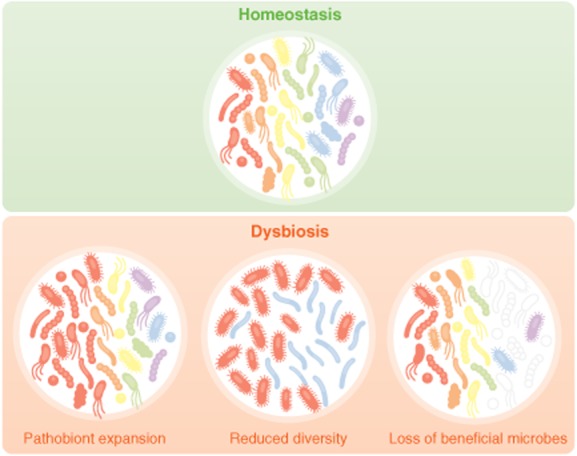
A loss of beneficial microbes, expansion of pathobionts, and loss of diversity are events that encompass dysbiosis. During healthy, homeostatic conditions the microbiota is composed of a diversity organisms that are known to benefit host development and health. However, environmental insults, such as antibiotic use or diet can lead to disruptions in the structure of the microbial community. These disruptions can lead to a loss of organisms that are beneficial to the host and a subsequent overgrowth of commensals that have the potential to cause harm, termed pathobionts. Domination of the microbiota by pathobionts can lead to inflammation and pathology. Additionally, multiple studies have described the diversity of contributions made by the various members of the microbiota. Oftentimes, these are non-redundant influences on host health, thus a total loss of diversity in the microbiota can also influence disease progression or severity and thus also represents a dysbiosis event.
