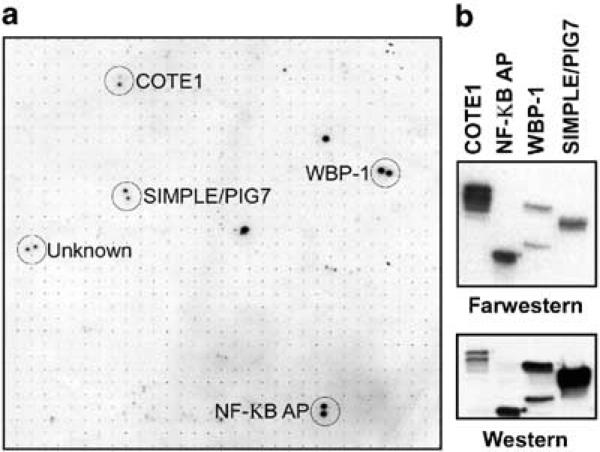
Figure 2.
Identification of candidate WWOX interacting proteins. (a) High-density protein arrays were probed with a 32P radiolabeled WW domain. Proteins bound to the WWOX WW domains were visualized by autoradiography and were identified by mapping their coordinates on the array grid. A partial view of the array is shown with duplicate positive colonies circled. The name of each protein identified by BLAST search is shown. (b) The interaction of the WWOX WW domains with the identified proteins was confirmed by far-Western analysis of bacterial expressed candidate proteins. Each candidate protein was bound to nickel agarose beads under denaturing conditions, separated by SDS–PAGE and transferred to PVDF membranes. Membranes were analysed by Western blotting (bottom panel) using antibodies that recognized the histidine tag, and by far-Western analysis (top panel) using radiolabeled WWOX WW domains as a probe