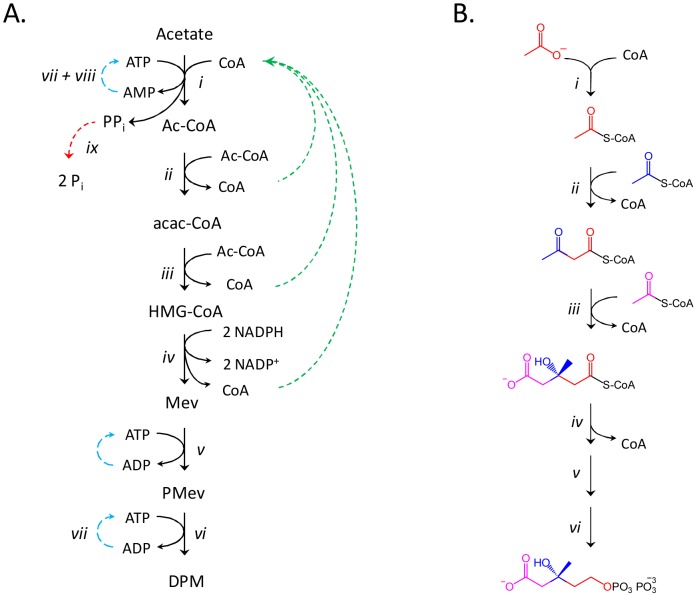
Figure 1. Schematics for the in-situ enzymatic synthesis of DPM and its isotopomers.
Panel A. The enzymatic synthesis of DPM from acetate and CoA. The synthesis occurs in six steps (i - vi). CoA is consumed at reaction i, and regenerated at steps ii-iv. To prevent product inhibition and thermodynamically bias the system toward DPM formation, ADP (vii) and AMP (vii and viii) are recycled and pyrophosphate is hydrolysed (ix). Panel B. The incorporation of acetate into DPM. Acetate fragments are enzymatically concatenated to form the 6-carbon skeleton of DPM. Isotopic labels can be introduced at various points in the DPM synthesis to achieve a particular labeling outcome. The enyzmes used in the synthesis are as follows: i, acetyl-CoA synthetase; ii, acetoacetyl-coA thiolase; iii, hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA synthase; iv, hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase; v, mevalonate kinase; vi, phosphomevalonate kinase; vii, pyruvate kinase; viii, adenylate kinase; ix, inorganic pyrophosphatase.