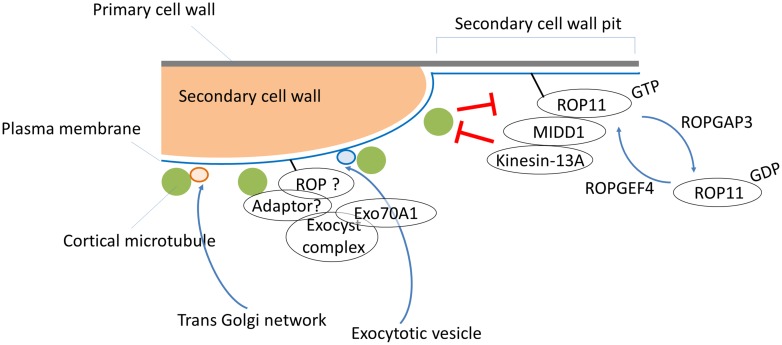
FIGURE 1.
A multi-Rho of plants (ROP) signaling model for secondary cell wall development. ROPGEF4 and ROPGAP3 establish the ROP11/MIDD1/kinesin-13A pathway to generate a cortical microtubule-absent area by promoting microtubule depolymerization, which results in pits of secondary cell walls in metaxylem vessels. Cortical microtubules restrict signaling from the ROP11/MIDD1/kinesin-13A pathway and promote local secondary cell wall deposition via an unknown ROP pathway and/or an ROP-independent pathway that controls targeting of exocytotic vesicles through EXO70A1. An adaptor protein such as RIP1/ICR1 might mediate interactions between the putative ROP, exocysts, and cortical microtubules. Vesicles from the trans-Golgi network are directly targeted to cortical microtubules, and subsequently supply cellulose synthase complexes to the cellular sites where microtubules are present.