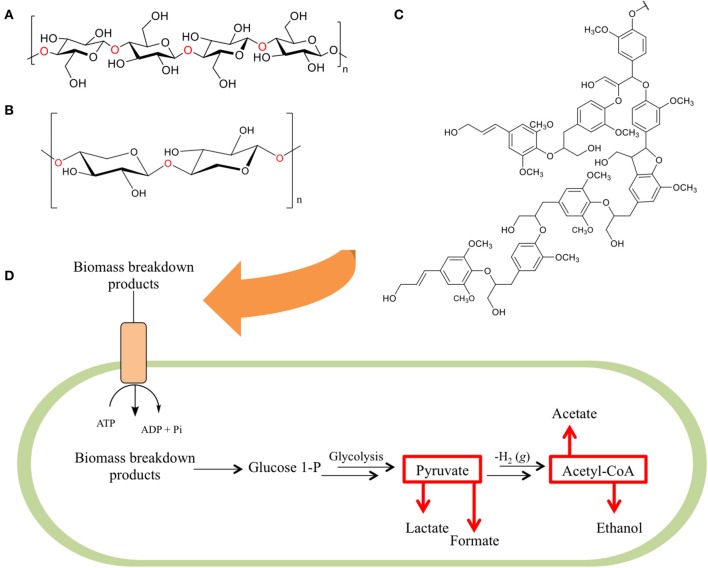
Figure 1.
The three primary constituents of biomass. Biomass is primarily composed of a combination of (A) cellulose—a homopolymer of glucose units, (B) hemicellulose (here depicted as xylan—a homopolymer of xylose units), and (C) lignin (here depicted as hardwood lignin)—a biopolymer composed of aromatic monomeric units. As these components are degraded (D) their fermentable breakdown products are shuttled into bacterial cells via ATP binding cassette transporter proteins and internally converted to glucose-1-phosphate (G1P). G1P is utilized in a modified form of glycolysis that produces pyruvate, which is then broken down into lactate and formate, or converted to acetyl-CoA and further metabolized to acetate and ethanol.