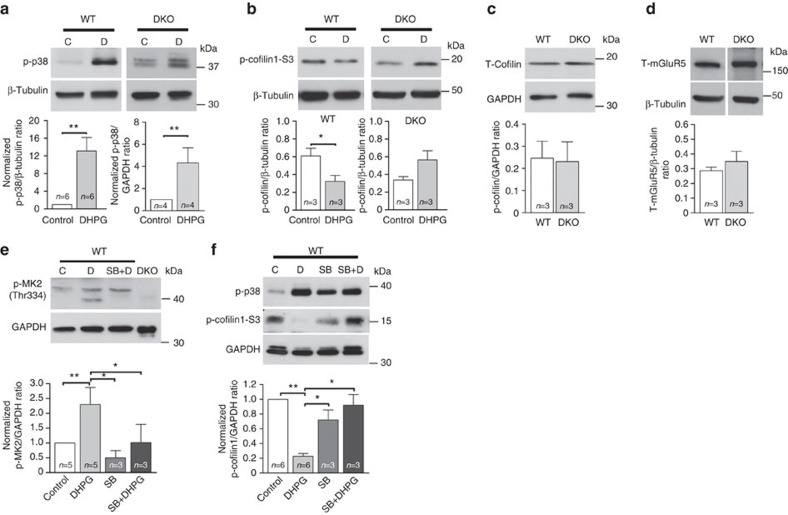
Figure 5. The p38-MK2/3-cofilin1 cascade is required in DHPG-LTD.
(a–f) Representative blots of non-stimulated (C), DHPG-incubated (100 μM, 10 min; D), pre-incubated with p38 inhibitor SB 203580 (5 μM) alone (SB) or pre-incubated with DHPG application (SB+D) cultures from WT and MK2/3 DKO hippocampus. (a) DHPG causes a significant increase in p-p38 at (Thr180/Tyr182) and (b) a significant reduction in p-cofilin1 in WT cells, an effect that is blocked in DKO cells. Note that no change in total cofilin1 (c) or mGluR5 (d) expression is detected between genotypes. (e) Blot showing a significant increase in phosphorylation of MK2 (Thr334) after DHPG-exposure in WT cells, an effect blocked by pre-incubation with SB. (f) Blot showing that the DHPG-dependent reduction in levels of p-cofilin1 (Ser3) is blocked by pre-incubation of p38 inhibitor SB 203580 (5 μM) in WT hippocampal cultures. Incubation of SB alone does not promote any significant changes in cofilin1 phosphorylation. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and β-tubulin were used as loading controls. Western blot band densitometry analyses were obtained from a minimum of three different primary hippocampal preparations from the WT and DKO mice. T-tests, one-way analysis of variance and the appropriate post-hoc test were conducted accordingly for each data set. Error bars indicate ±s.e.m. and *P<0.05, **P<0.01.