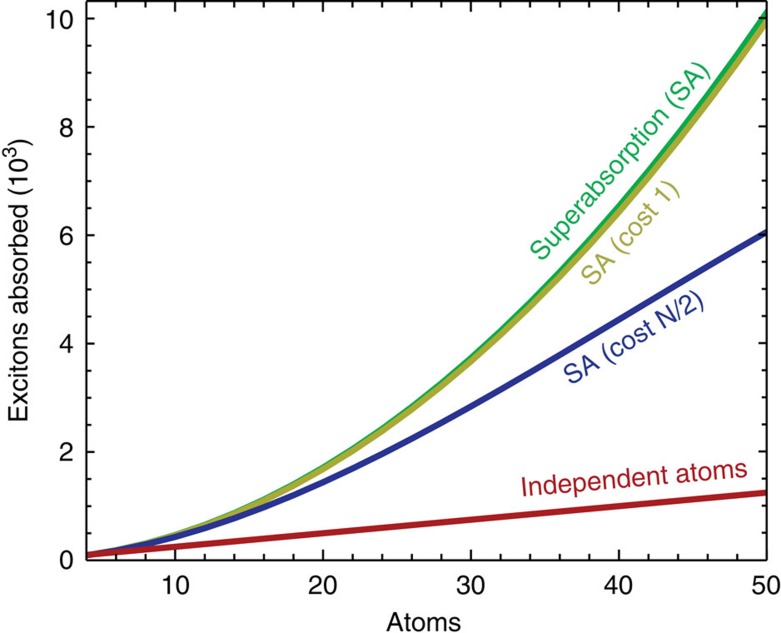
Figure 5. Superlinear exciton absorption.
The total number of excitons absorbed within the common reference time 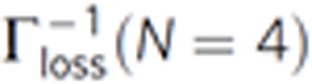 as a function of the number of atoms N. The coloured curves represent the reinitialization cost models described in the main text, and the red line shows the maximum extracted from independent atoms for comparison. The scaling is superlinear in all coupled atom cases, approximately following the ideal N2 law (green), except for large N in the pessimistic cost model of full reinitialization (blue). If quantum feedback control enables the replacement of a single exciton as soon as a loss event has happened, then the nearly quadratic scaling persists up to an arbitrary number of atoms (olive).
as a function of the number of atoms N. The coloured curves represent the reinitialization cost models described in the main text, and the red line shows the maximum extracted from independent atoms for comparison. The scaling is superlinear in all coupled atom cases, approximately following the ideal N2 law (green), except for large N in the pessimistic cost model of full reinitialization (blue). If quantum feedback control enables the replacement of a single exciton as soon as a loss event has happened, then the nearly quadratic scaling persists up to an arbitrary number of atoms (olive).