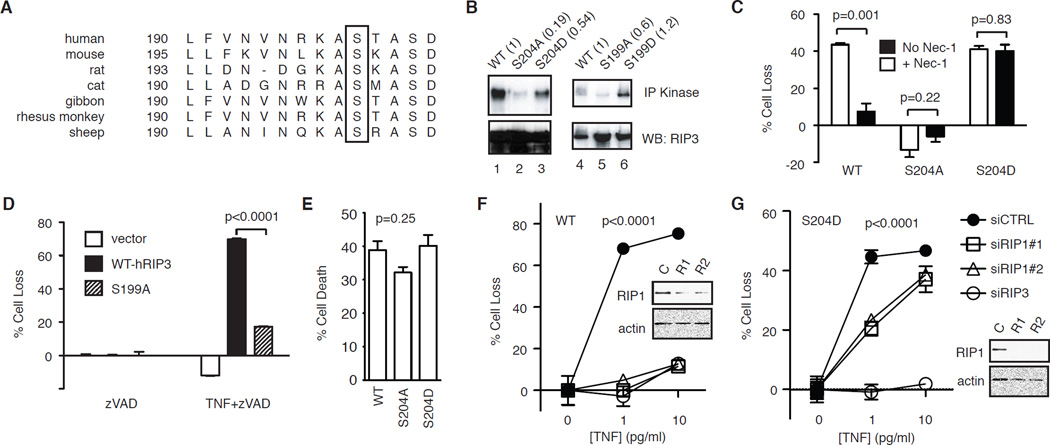
Figure 3. Ser204 critically regulates RIP3 function.
(A) Sequence alignment of RIP3 reveals conservation of Ser204 (in mouse RIP3) among different species (box). (B) Effects of alanine and aspartic acid substitution of Ser204 on mRIP3 and Ser199 on hRIP3 kinase activity. The indicated RIP3-GFP fusion proteins were expressed in 293T cells were subjected to in vitro kinase assay. The numbers in parentheses represent the normalized kinase activity compared to wild type RIP3. (C) RIP3−/− fibroblasts stably expressing the indicated RIP3-GFP fusion proteins were treated with TNF and zVAD to induce programmed necrosis, with or without 1 µM Nec-1. (D) The indicated RIP3-GFP plasmids were transfected into RIP3−/− fibroblasts and tested for TNF and zVAD-induced programmed necrosis. (E) RIP3−/− fibroblasts stably transfected with the indicated RIP3-GFP plasmids were tested for TNF and cycloheximide (CHX) induced apoptosis. One-way ANOVA analysis was performed to compare the three different groups. (F-G) RIP3−/− fibroblasts stably expressing the indicated WT or S204D RIP3-GFP fusion protein were transfected with the indicated siRNAs. TNF and zVAD-induced programmed necrosis was determined. Western blots show the level of silencing by the RIP siRNAs. Two-way ANOVA analysis was performed.