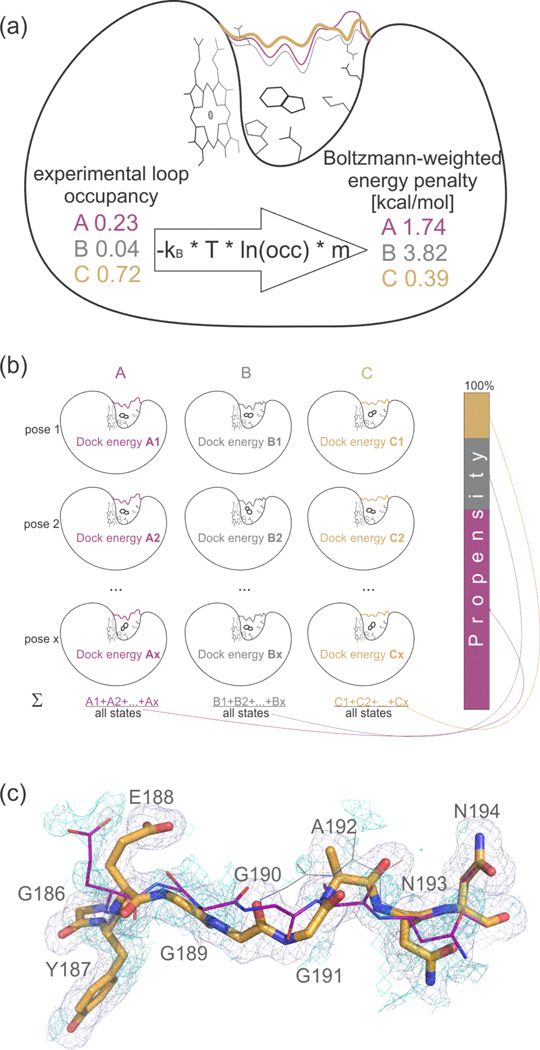
Figure 1. Experimental occupancies of Apo loop conformations set penalties for docking.
(a) From experimental loop occupancies to docking penalties.
Flexible loop (in colors) and side-chain conformations of the Apo CcP Gateless protein are assigned Boltzmann-weighted energy penalties based on their crystallographic occupancy; kB – Boltzmann constant, T – temperature in K, occ. – occupancy, m – flexible weighting multiplier (here m = 2).
(b) From docking energies to loop propensities.
The Boltzmann sum of the energies of all x poses for a ligand to different loops A, B, C are calculated. The result is expressed as a percentage, indicating the predicted preference of the ligand to bind to a particular loop conformation, that can be compared to the experimental occupancies.
(c) Electron density shows evidence for 3 conformations of the apo loop.
Electron density showing missing conformation of loops A (purple sticks) and B (grey lines) when only loop C (orange sticks) is included in the refinement is shown as blue (2mFo-DFc, 1sigma) and cyan (Fo-Fc, +1.5sigma). Stick radius according to relative occupancies (cf. Figure 2A). See Suppl. Figure 13 for more pronounced difference cyan density for loop B when including A in addition to C in refinement.