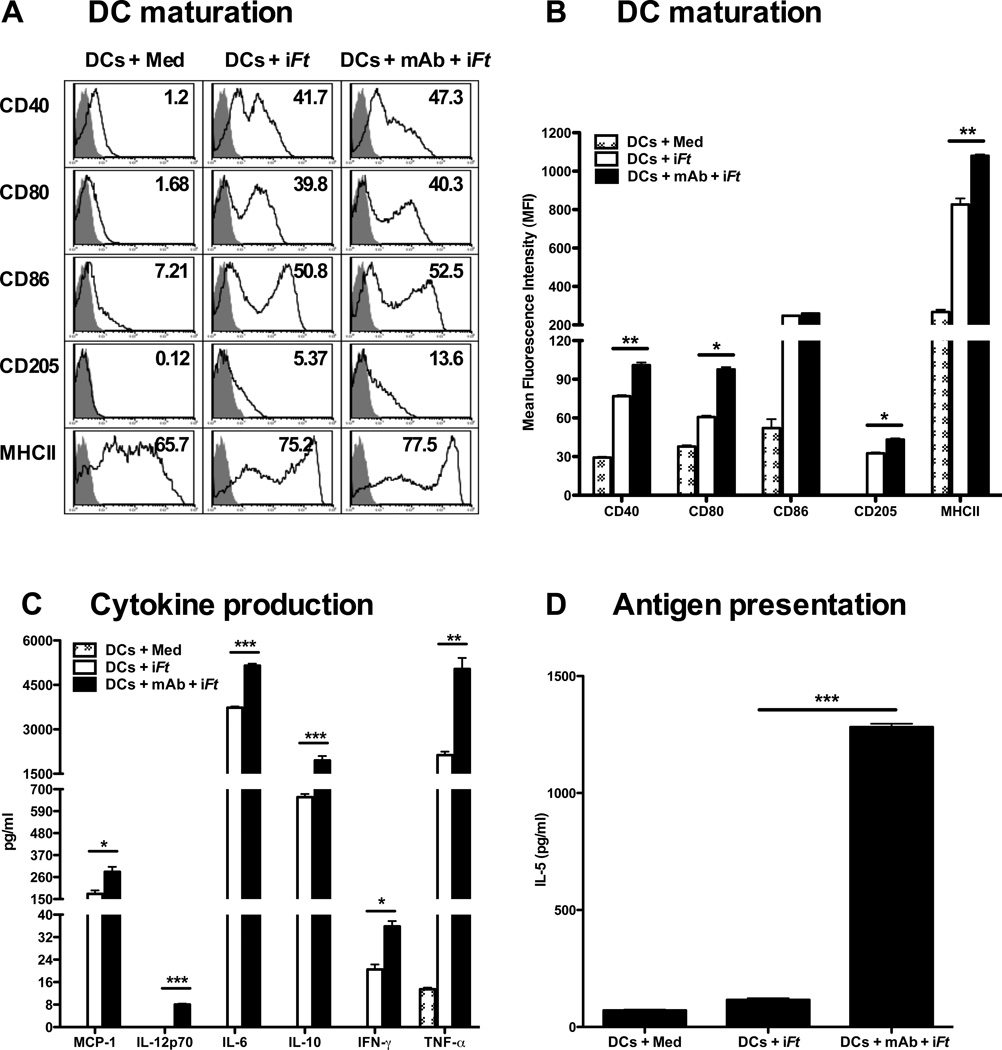
Figure 2. Pulsing BMDCs ex-vivo with mAb-iFt enhances in vitro iFt-induced BMDC maturation and Ag presentation.
BMDCs (5 × 105) were pulsed overnight with medium or iFt (10 iFt/cell) in the presence or absence of mAb (1 µg/ml). Cells were then washed and stained for DC maturation markers. Acquisition was performed using an LSRII flow cytometer and data was analyzed using FlowJo software (Tree Star). (A) The grey peak represents isotype controls. Numbers in the right hand corner of each histogram indicate percent positive cells for the indicated DC maturation marker. (B) The maturation data are analyzed and expressed as Mean Fluorescence Intensity (MFI). Data in A and B are representative of four independent experiments. (C) BMDCs (2 × 105) were stimulated with medium or iFt (100 iFt/cell), in the presence or absence of mAb (1µg/ml) for 3 days. Culture supernatants were then collected on day 3 and screened for cytokines using the Luminex assay. Data presented are from a single experiment, but are representative of results from three independent experiments. (D) BMDCs were stimulated overnight with medium or iFt (2.5 iFt/cell) in the presence or absence of mAb (1 µg/ml). Pulsed BMDCs were then washed 3 times with medium and co-cultured with an Ft-specific T cell hybridoma (FT256D10) for 24 hours. Culture supernatants were subsequently harvested and assayed for the presence of IL-5, a cytokine secreted by this T cell hybridoma in response to Ag recognition. Figures presented are from single experiments and are representative of results from three independent experiments. Data are presented as the average of three replicate samples ± SD (*: P< 0.01, ** P< 0.005, *** P<0.0005).