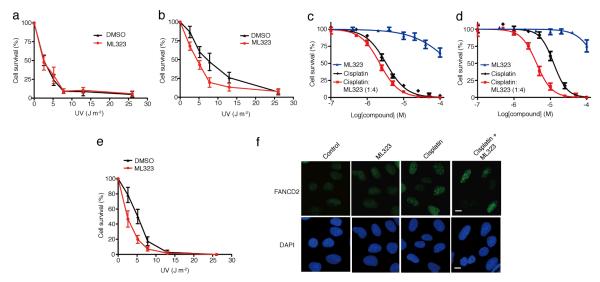
Figure 4. The effect of inhibiting USP1-UAF1 by ML323 in the TLS and FA pathways.
(a,b) Colony-forming assay of XPV cells (a) and XPV + Polη cells (b) irradiated with UV alone (black) or a combination of UV and 20 μM ML323 (red). The data represent the mean ± s.d. of three independent experiments. (c,d) Cytotoxicity assay of PD20 cells (c) and PD20 + D2 cells (d) treated with cisplatin alone (black), ML323 (blue) or a combination of cisplatin with ML323 at a ratio of 1:4 (red). The data represent the mean ± s.d. of three independent experiments. (e) Colony-forming assay of PD20 cells irradiated with UV alone (black) or a combination of UV and 20 μM ML323 (red). The data represent the mean ± s.d. of three independent experiments. (f) Comparison of FANCD2 foci formation in U2OS cells treated with 30 μM ML323, 5 μM cisplatin or a combination of 30 μM ML323 and 5 μM cisplatin. Scale bars, 10 μm. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.