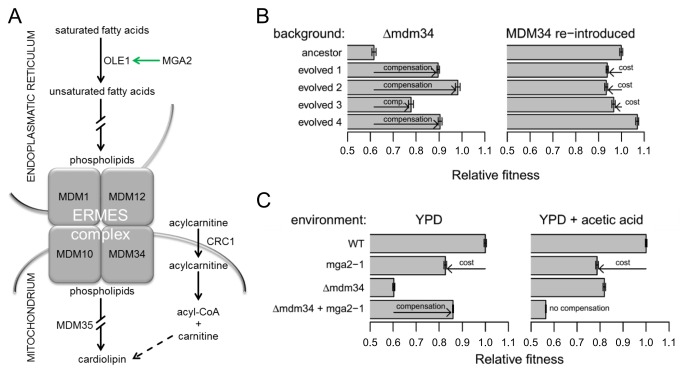
Figure 6. Compensation of the MDM34 gene deletion.
(A) The cardiolipin synthesis pathway with an emphasis on the ERMES complex. The complex tethers the endoplasmatic reticulum to the mitochondria, and is central for the transfer of phospholipids between the two compartments. De novo mutations in the independent evolutionary lines affected different, but related cellular subsystems, including upregulation of the unsaturated fatty acid synthesis (MGA2), another step of the cardiolipin synthesis pathway downstream of the ERMES complex (MDM35), and another mitochondrial transport process (CRC1), which most likely affects respiration by modulating the interaction between carnitine and cardiolipin. For further details on the underlying mechanisms see Text S1. The green arrow represents transcriptional upregulation; the dashed arrow indicates indirect positive effect. The mutations in MGA2, MDM35, and CRC1 genes were found in Δmdm34 evolved lines 1, 3, and 4, respectively. (B) The cumulative fitness effects of the compensatory mutations in Δmdm34 and “wild type” (Δmdm34+MDM34 reintroduced) backgrounds (Table S7). (C) Epistatic interactions between mutations in two environments (Table S7). The bars in (B) and (C) indicate means ± standard error. Arrows indicate fitness costs and the extent of compensation.