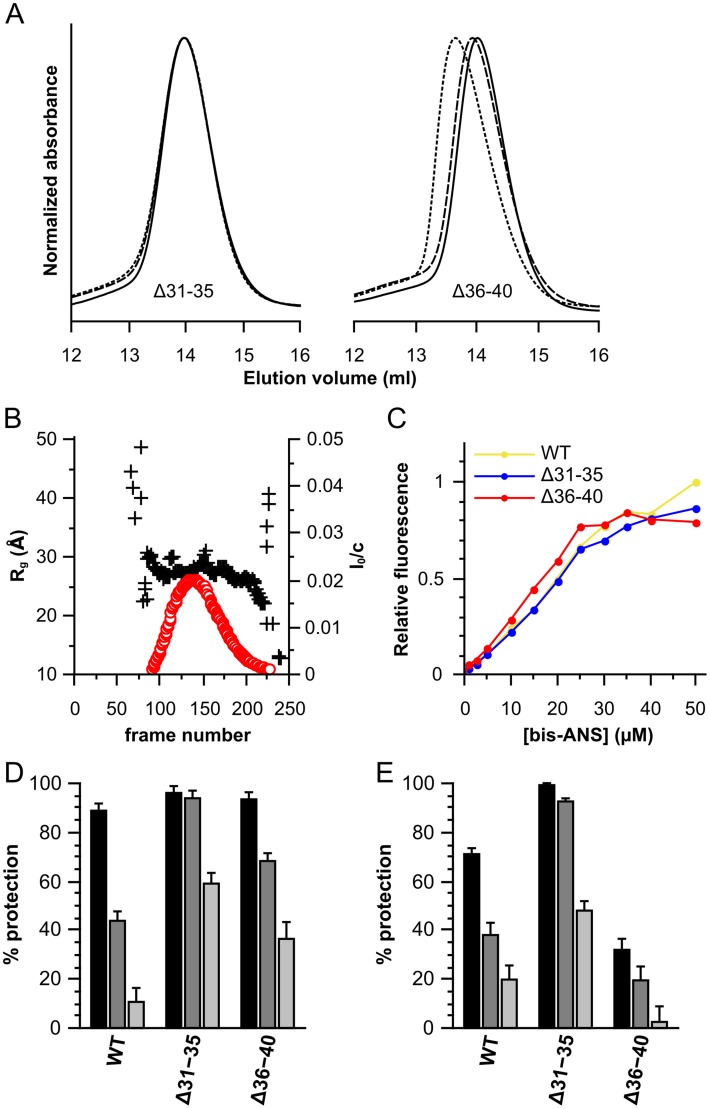
Figure 7. Characterization of the Δ31–35 and Δ36–40 deletion constructs of HSPB6.
(A) Size-exclusion chromatography profiles, 100 µl of protein was loaded onto a Superdex 200 10/300 GL column at different concentrations. 2.5 mg/ml is shown as a solid line, 5 mg/ml as a dashed line and 10 mg/ml as a dotted line. The absorbance was normalized to the maximum for each curve. (B) SAXS analysis of Δ31–35. 250 frames were collected during elution from a Shodex KW-404F column. The radius of gyration (Rg) and forward scattering (I0) were calculated at each measured point using buffer subtracted scattering curves that had been averaged by a ten-frame moving average algorithm to improve the signal-to-noise. The forward scattering values are normalized by dividing the values by the concentration of the sample at the peak maximum. The Rg is plotted as a black cross and scaled on the left axis, the I0 is shown as a red circle and scaled on the right axis. (C) Bis-ANS titration curves. 2.5 µM of protein was incubated with increasing concentrations of bis-ANS and fluorescence intensities were recorded at 490 nm with an excitation wavelength of 390 nm. HSPB6 is depicted in yellow, Δ31–35 in blue and Δ36–40 in red. (D) Chaperone-like activity using insulin as a substrate, the monomer mass molar ratios tested were 1∶0.2 (black), 1∶0.1 (dark gray) and 1∶0.05 (light gray). (E) Chaperone-like activity using yADH. The ratios used are 1∶2 (black), 1∶1 (dark gray) and 1∶0.5 (light gray).